•Antioxidants prevent oxidative stress
•Two types of antioxidants -enzymatic and non-enzymatic
•Reaction Age (technical tidbit)
- Preventing cellular damage that initiates many diseases
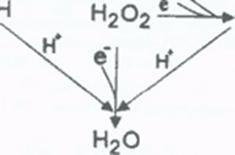
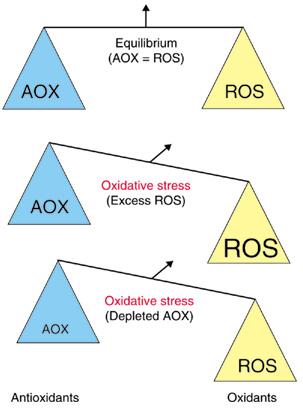
Antioxidants are needed to balance the oxidants produced by and present in the body -normal biological activities of aerobic cells and organisms continuously generate oxidants (e.g. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), including Free Radicals) which can inflict cellular damage when they are generated to the extent that they overwhelm the cells'ROS "Damage control"antioxidant systems.Oxidant / antioxidant balance i.e. maintaining oxygen homeostasis (stability), is the major factor in maintaining good cellular function and preventing oxidative stress, which plays a significant role in the progression of many diseases, including diabetes, Alzheimer disease, and atherosclerosis/heart disease.

To prevent damage to cells in the body from excess ROS, there must be a balance between the formation of necessary oxidant ROS and the ability of the body's antioxidant defense to remove them.
For information on the two "faces"of ROS:
Life's Oxygen Paradox - Meet Dr. ROS Jeckyll and Mr.ROS Hyde
Antioxidants sacrifice themselves to preserve your body parts - basically, antioxidants are molecules that ROS, such as free radicals, find "more attractive"than cellular components. Antioxidants readily donate their electrons to prevent free radicals from stealing electrons out of membrane fatty acids, mitochondria, DNA, and elsewhere.
After donating an electron, an antioxidant becomes a free radical by definition. Antioxidants in this state are not harmful because they have the ability to accommodate the change in electrons without becoming reactive themselves.
Antioxidants each work in their own unique manner and in their particular area of expertise, but they also complement each other - in a wonderful synergy that effectively protects cells from free radicals.
"When vitamin E disarms a free radical, it becomes a weak free radical itself. But unlike other free radicals, the vitamin E radical can be recycled, or turned back into an antioxidant, by vitamin C or coenzyme Q10. These network antioxidants will donate electrons to vitamin E, bringing it back to its antioxidant state."
- Dr. Packer, author of "The Antioxidant Miracle"
Healthy cells and aerobic organisms have more protective antioxidant enzymes (E.g. SOD, CAT and Glutathione peroxidase)than anaerobic organisms - which are thus more vulnerable to oxidative damage.
There are two types of antioxidant protective mechanisms against oxidative stress
1. Enzymatic Antioxidants
2. Non- Enzymatic Antioxidants
All Antioxidants need optimal amounts of certain dietary, MINERALS to function properly
Refers to the minimum distance away a free radical scavenger must be from a radical to be able to neutralize the radical.
E.g. OH•
travels no more than several Angstroms before it interacts with another molecule
and a free radical scavenger must be within this
"cage" to neutralize the radical. Thus, for example,
if an antioxidant is confined to the lipid-rich
membrane of a cell because of its specific solubility, it will be ineffective in
reducing OH•
damage to DNA in the nucleus.