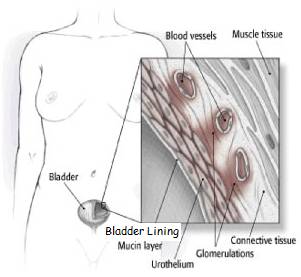
IC begins with the irritation and eventual erosion of the interstitial lining of the bladder. Consequently, the interstitial tissue in the space between the normally-protective bladder lining and the bladder muscle becomes chronically inflamed. This manifests as pelvic pain, and a frequent, urgent feeling, described as a "hot poker" on the bladder wall or "razor blades in the bladder".
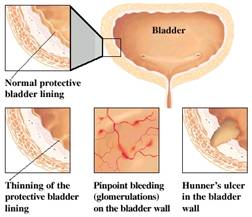
Pin-point bleeding (glomerulations). Diagnostic cytoscopy with hydrodistention shows tiny hemorrhages on the bladder lining as a result of the damaged interstitial tissue.
Tiny ulcers. The lining can deteriorate to the point of becoming ulcerated. The resulting so called Hunner's ulcers are super-sensitive and extremely aggravated by overly-acidic urine.