
LASER is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
A red/near infrared (NIR)frequency of light (~700-1000 nanometers) is applied via a class 4 laser to problem areas of the body at an appropriate dosage and power level. SImilar to Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT, aka cold laser therapy), this therapy is also referred to as photobiomodulation, whereby laser energy is absorbed by specific chromophores in the body:
The overall functional effects are:
In contrast to LLLT, the higher wattage utilized in class 4 laser therapy also produces a mild photothermal effect, which aids vasodilation, muscle relaxation and nerve conduction. Note that an excessive photothermal effect can damage tissue.
Infrared Class 4 laser therapy produces biomodulating reactions that can very effectively:
By definition a class 4 laser must be able to deliver power of at least ½ a watt (i.e. 500 milliwatts). Unfortunately this category does not distinguish between the different power levels required for cosmetic / hair-removal use, healing, surgical lasers or even military lasers (capable of shooting down a satellite!).
Infrared class 4 lasers were FDA-approved in 2005 as medical therapy devices (class 3 lasers were FDA-approved in 2002):
| Some class 4 lasers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand | Specs. (CW=continuous wave) | Cost | |
 |
K-laser (still available, but no longer produced). |
K-800. 0.1 - 8 watts K-1200. 0.1 - 12 watts CUBE-4. 0.1 - 15.0 watts (CW) & 20 watts peak / av. 12 watts pulse |
|
|
Summus lasers (K-laser rebranded in 2019) |
P-4. 0.5-24 watts in continuous mode or 28 watts peak / av. 15
watts pulse. 4 wavelengths (650nm, 810nm, 915nm and 980nm); P-3. Up to 18 watts; 3 wavelengths (650nm, 810nm, 915nm), H1. 15 watts; 3 wavelengths (650nm, 810nm, 915nm); 1-20,000Hz pulse; Lenses: 50mm broadbeam, 25mm zoom |
||
 |
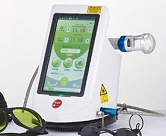
Eltech Klaser Cube 4 plus by Chattanooga (Made in Italy |
12-15 watts 4 wavelengths (660nm, 800nm, 905nm, 970 nm) Intense Super Pulse (ISP) & CW |
~$20-28k |
 |
EVOlaser | 9 - 20 watts Up to 4 Wavelengths Pulse & CW |
~$10-15k |
 |
Pilot Laser | 9 watts 810nm Pulse & CW |
~$8k |
 |
Apollo Laser | .5 - 5 watt 810nm CW |
$5k and up |
The high-power of the class 4 laser enables it to penetrate deep enough into the body to reach muscles, and areas such as spine and hip
Some examples of health problems healed by class 4 laser treatments:
How to obtain class 4 laser treatment
In addition to power level, the laser wavelength determines penetration depth (note that wavelength is inversely proportion to its frequency)
Energy from 400-1100nm wavelength photons are specifically absorbed by chromophores in the skin (including melanin, blood and water). Chromophores convert light energy to kinetic energy in mitochondria and cell membranes of cells (E.g. fibroblasts) located up to ~4cm depth into the body. Scattered photons from a Class 4 infrared laser produce an egg-shaped treatment area in tissue. The ability of infrared lasers to target chromophores is utilized in cosmetic therapies such as hair removal, skin resurfacing, and treating age spots, rosacea, and vascular lesions / broken blood vessels.
Primary reactions precipitate a cascade of metabolic changes resulting in physiological changes to cells. E.g. changing membrane permeability, release of calcium from mitochondria to change cell's intrarcellular levels. This in turn stimulates cell metabolism and regulates signaling pathways needed for wound repair, such as cell migration, RNA/DNA synthesis, cell mitosis, protein secretion, and cell proliferation.
Secondary events induce distant effects. Affected /energized cells communicate with each other and non-irradiated cells via increased levels of cytokines and/or growth factors. This leads to an increased immune response to control inflammatory healing (activates T-cells, macrophages, several mast cells, and increases endorphin synthesis / decreases bradykinin to control pain)
You can search the web to find a provider near you.
Depends on type of condition:
The effects of class 4 laser treatments are cumulative.
Pain relief is typically achieved before healing occurs. It is therefore necessary to stay with the therapy if you want complete healing that deals with the cause of the problem
Treatment times are just a few minutes
Class 4 laser therapy is painless. Although the patient may feel some slight, relaxing warmth
Cost is around $55-75 /treatment (2019 prices)
The class 4 laser should not be used:
One should wait at least seven days after having a cortisone (corticosteroid / steroid) shot. Since both steroids and Class 4 laser therapy suppress prostaglandin E-2 (which otherwise has a hormone-like effect to promote inflammation in its local area)
Light sensitive medication may be affected by laser therapy.
Class 4 therapy lasers are safe to use over metal implants. Tissue warming occurs from the outside-in.
A Class 4 therapy laser is used by someone trained to understand and practise safety precautions for handling this powerful device.
The FDA requires wavelength-specific safety goggles for everyone in the treatment room to protect eyes. SInce infrared lasers are outside the visible spectrum, the blink reflex will not register. The Nominal Hazard Zone (NHZ) is defined as "the space within which the level of the direct, reflected, or scattered radiation during normal operation exceeds the applicable MPE." The NHZ for Class 4 therapy lasers is about 21 feet.
The FDA also requires that one person be designated as the "Laser Safety Officer" for the treatment facility.
Dosage refers to the amount of energy per unit area of tissue surface exposed to laser beam. Measured as Joules / cm2. The power of a laser is the rate of energy being delivered (usually measured in watts) 1 watt is 1 Joule / second, so a laser operating at 8 watts power level, with a continuous wave would deliver 480 joules in 1 minute, and 240 Joules/min in pulsed mode (with 50% duty cycle). In 1 minute, a treatment area of 50cm2 (~8 inches2) would therefore receive a dose of 9.6 J/cm2 (480 J /50cm2) in continuous mode, or 4.8 J/cm2 in pulsed mode.
Required dosage is affected by several factors: including wavelength of beam, tissue type /condition, whether problem is acute or chronic, skin pigmentation, treatment method.
There's a "Goldilocks" dosage window. Below this window, biostimulation does not occur, and above the window, it is inhibited or can cause damage to tissue. This has been easily observed in wound healing and hair growth (Tuner & Hobe, 2004). Biostimulation is reported in the dosage range of 0.001 to 10 J/cm2.
When treating with a GaAlAs diode laser, the current accepted dosage for deep-lying pain is 4-10 J/cm2. (Ibid Tuner & Hode, 2004).
Output wattage. A deeper target requires a higher wattage to enable sufficient photons to reach the target to yield the primary effects of photobiomodulation. Examples (adjusted by clinical laser therapist according to his or her judgement):
Much of the beam energy is reflected, or scattered into none-targeted areas. An estimate of at least half of the energy is lost when targeting an area well below the skin.
Applying a combination of continuous wave and various frequencies of pulsation is the best treatment approach. Using different pulse frequencies prevents the body from getting immune to and becoming less responsive to any steady stimulus. (Blahnick & Rindge, 2003)
The treatment wand is kept in motion during the continuous wave phase, and is pressed into the tissues for several seconds during laser pulsation.
Empirical evidence provides a guide for which pulsation frequency ranges to use for specific problems and tissues:
Ideally - Class 4 laser therapy combines several of these pulsation frequencies to provide an analgesic effect, inflammation reduction, and biostimulation.
Bayat M, Ansari A, and Hekmat H (Sep 2004) Effect of low-power helium-neon laser irradiation on 13-week immobilized articular cartilage of rabbits. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 42(9): 866-870.
Blahnick J and Rindge D. Laser Therapy, A Clinical Manual. 2003. Healing Light Seminars, Inc. Melbourne, FL. p 27.
Jia YL and Guo ZY (2004) Effect of low-power He-Ne laser irradiation on rabbit articular chondrocytes in vitro. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. 34(4): 323-328.
Moore P, Ridgeway TD, Higbee RG, Howard EW, and Lucroy MD (2002) Effect of wavelength on low intensity laser irradiation — stimulated cell proliferation in vitro. Lasers Surg Med. 36(1): 8-12.
Tuner J and Hode L (2004) The Laser Therapy Handbook. Prima Books. Grängesberg, Sweden. pp 72-74.