SUPPORTING_INFORMATION/CELL_MESSENGERS/HORMONES/STEROIDS/SEX/ESTROGENS/HB/ESTROGENS_HB_MAIN.html
| Estrogen (mainly ESTRADIOL) has numerous effects in the body | |
|---|---|
|
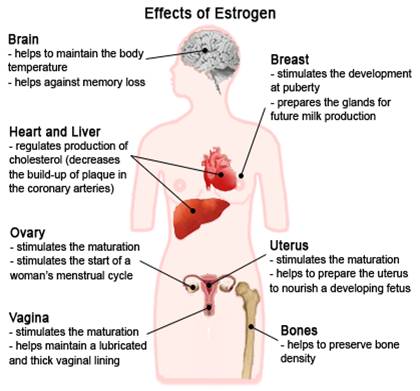
Sex Differentiation |
▪ Promotes formation of female secondary sex characteristics: growth of a girl's sex organs, breasts and pubic hair. |
|
▪ Effeminization when estrogen to TESTOSTERONE ratio increases. E.g. Breast growth, higher voice, loss of body hair, decrease in muscle mass, increase in fatty tissue, prostate enlargement, change in sex drive; |
|
|
Protein Synthesis |
▪ Estrogen action: The role of specific RNA and protein synthesis; |
|
Reproductive Functions |
▪ Decreases libido (sex drive); ▪ Helps regulate menstrual cycle; ▪ Stimulates endometrial growth; ▪ increases uterine growth; ▪ ESTRIOL produced by placenta is involved with maintaining pregnancy and initiating labor. ▪ Breast-feeding stimulates estrogen production - which stimulates production of the PROLACTIN hormone to increase milk production. |
|
▪ ESTRADIOL modulates sex drive, erectile function and spermotogenesis in men - for libido, estrogen is to men what TESTOSTERONE is to women. Estrogen receptors and aromatase (enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen) are abundant in brain, penis, and testes, organs important for sexual function. In the brain, estradiol synthesis is increased in areas related to sexual arousal. PubMed
|
|
|
Reproductive organ cancers |
▪ Promotes hormone-sensitive reproductive organ cancers - treatment of endometrial and breast cancer involves suppression of estrogen production; ESTRADIOL promotes an oncogene, Bcl-2 (expressed at high levels, oncogenes help turn a normal cell into a tumor cell). ▪ ESTRADIOL increases expression of genes that are responsible for directing production of both androgen and estrogen hormone receptors. |
|
Regulates Fluid balance |
▪Regulates salt / water retention; ▪ Increases growth hormone; ▪ Increases CORTISOL, SHBG (Sex-Hormone Binding Globulin) -binds ESTRADIOL (and TESTOSTERONE) in blood and thus inhibits their bioavailability, since only "free"hormones are active) |
|
Structural |
▪ Accelerates height growth; ▪ Reduces muscle mass; ▪ Maintains blood vessels /skin; |
|
Shortened height |
▪ Can cause early epiphseal closure near the end of puberty - thus limiting height |
|
Protects against heart disease / Blood Clotting |
▪ Increases HDL & triglycerides / Decrease LDL & fat deposition in coronary arteries; ▪ Blood Coagulation - Increase circulating level of factors 2, 7, 9, 10, antithrombin III, plasminogen / Increase platelet adhesiveness |
|
GI Tract |
▪ Reduces bowel motility; ▪ Increases cholesterol in bile; |
|
Lungs |
▪ Promotes lung function by supporting avioli |
|
Preserves bone density |
▪ Helps decrease bone loss slightly - by slowing bone resorption (osteoclast activity); antagonizes the effects of PTH, minimizing the loss of calcium from bones, |
|
Decreases fat burning |
▪ Increases subcutaneous fat deposits/decreases fat-burning by stimulating SNS. As an Alpha 2 adrenergic agonist, estrogen increases/activates Alpha2 adrenoceptors (A2As), which inhibit fat burning (A2As react to neurotransmitters EPINEPHRINE, NOREPINEPHRINE, and isoprenaline, for a sympathetic effect; NOREPINEPHRINE is one of the body's primary fat burning agents), but when estrogen binds to the A2A (taking NOREPINEPHRINE's "seat"), it creates a negative feedback loop inhibiting the release of fat-burning NOREPINEPHRINE. |
|
Melanin |
▪ Increases pheomelanin, reduces eumelanin |
|
Anti-aging for Skin |
▪ Prevents decrease in skin collagen in post-menopausal women. Topical and systemic estrogen therapy increases skin collagen content / skin thickness/ skin moisture (increases acid mucopolysaccharides and hyaluronic acid, and possibly maintains stratum corneum barrier function); Possible anti-wrinkle effect on elastic fibers; |