Neurotransmitters are produced by the nervous system and released from the presynaptic nerve terminal in the brain, work locally and are fast. In contrast, hormones are produced by the endocrine glands, and usually released into the bloodstream to act on distant cells. Some hormones are also neurotransmitters, for example MELATONIN, SEROTONIN,, EPINEPHRINE (ADRENALINE), and NOREPINEPHRINE, which can be produced in the brain (as well as other locations) and then released into circulation.
Myelin sheath. Consists of Schwann cells that encircle axon like a jelly roll, act as insulators and are separated by gaps of unsheathed axon called Nodes of Ranvier. Instead of a continuous traveling down the axon, the action potential jumps from node to node (called saltatory conduction), thereby speeding up propagation of impulse.
E.g. ACETYLCHOLINE, DOPAMINE, GABA, GLUTAMATE, NITRIC OXIDE, SEROTONIN
See CHART of neurotransmitters for the different categories of the more common NTs at end of article
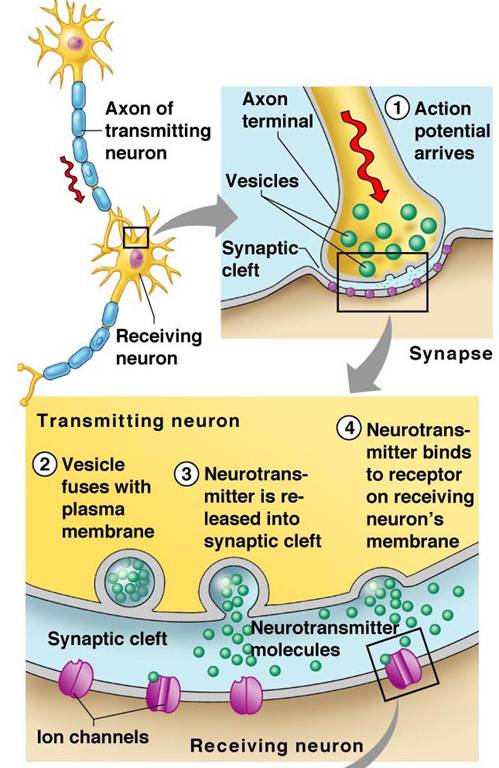
Neurotransmitters are usually released following arrival of an action potential at the synapse. This causes the voltage across the cell membrane (membrane potential) of a cell (in this case a presynaptic neuron) to rapidly rise and fall.
Neurotransmitters are made via just a few biosynthetic steps, from simple precursors, such as amino acids readily available from diet.
Have excitory or inhibitory effect (or both), depending only on the type of receptors they activate . An excitory effect increases the probability that the target cell will fire an action potential.
Types of Neurotransmitters (packaged in neurotransmitter vesicles, which are membrane enclosed sacks that store and release neurotransmitters into synapse at presynaptic neuron terminal so that they can be detected by receptors on the postsynaptic neuron)
Re-uptake of neurotransmitters
For nerve cells to communicate, neurotransmitters are secreted by one neuron and picked up by receptor proteins on the surface of another neuron. Once the message has been delivered, a neurotransmitter is either destroyed or reabsorbed into the cell that made it and its activity is over. This process is known as re-uptake.
Most psychoactive drugs exert their effects by altering the actions of some neurotransmitter systems. E.g. Addictive drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, primarily affect the DOPAMINE system. Addictive opiate drugs primarily indirectly regulate DOPAMINE levels.

Chart of some common neurotransmitters(Note that some neurotransmitters are also hormones) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Neurotransmitter | Abbr | Details | |
| Amino Acids (Small molecule) | ASPARTATE | |||
| GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID | GABA | |||
| GLUTAMATE | GLU | |||
| GLYCINE | GLY | |||
| Acetylcholine (Small molecule) | ACETYLCHOLINE | ACh | ||
| Purine (Small molecule) | ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE | ATP | ||
| Monoamines (Small molecule) | Phenylalanine/Tyrosine | DOPAMINE | DA | |
| EPINEPHRINE (ADRENALINE) | EPi, Ad | Hormone | ||
| NOREPINEPHRINE (NORADRENALINE) | NE, NAd | Hormone | ||
| OCTOPAMINE | ||||
| TYRAMINE | TYR | |||
| Tryptophan | SEROTONIN | 5-HT | Hormone | |
| MELATONIN | MEL | Hormone | ||
| Histamine | HISTAMINE | H | Hormone | |
|
Polypeptides (PP) - single linear chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds |
Gastrins | GASTRIN | ||
| CHOLECYSTOKININ | CCK | |||
| Neurohypophyseal | VASOPRESSIN, | AVP | ||
| OXYTOCIN | OT | |||
| NEUROPHYSIN I AND II | ||||
| Neuropeptide Y | NEUROPEPTIDE Y | NY | ||
| PANCREATIC POLYPEPTIDE | PP | |||
| PEPTIDE YY | YY | |||
| Opioids | CORTICOTROPIN | ACTH | ||
| DYNORPHIN | ||||
| ENDORPHINS | Resemble opiate drugs in structure / effects; contribute to pain-relief and "feel good" emotions | |||
| ENKEPHALINE | ||||
| Secretins | SECRETIN | |||
| MOTILIN | ||||
| GLUCAGON | ||||
| VASOACTIVE INTESTINAL PEPTIDE | VIP | |||
| GROWTH HORMONE RELEASING FACTOR | GHRF | |||
| Somatostatins | SOMATOSTATIN | |||
| Tachykinins | NEUROKININ A AND B | |||
| SUBSTANCE P | Responsible for transmission of pain (from certain sensory neurons to the CNS | |||
| Other | BOMBESIN | |||
| GASTRIN-RELEASING PEPTIDE | GRP | |||
| Soluble Gases | CARBON MONOXIDE | CO | ||
| NITRIC OXIDE | NO | |||
| Other | ANANDAMIDE | |||
| ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE | ATP | |||