(Pronounced "Sammy" / S-adenosyl methionine)
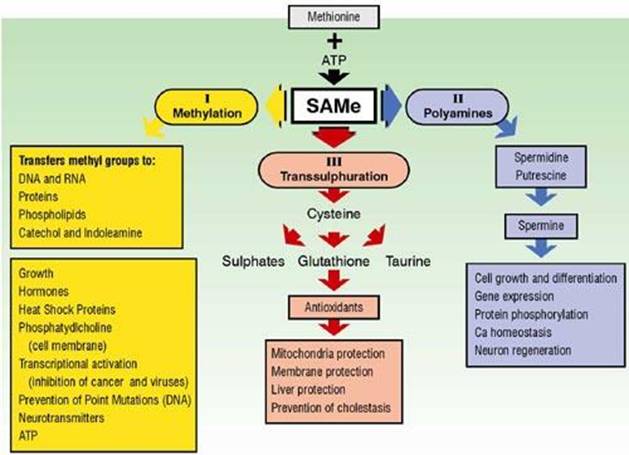
SAMe provides an IMPORTANT precursor molecule to 3 main pathways of all cellular metabolism: Transmethylation, transulfuration, and aminopropylation - A sufficiency of SAMe sustains their normal function, which depends on the daily availability of methionine obtained mainly from breakdown of dietary proteins or synthesized by the body (involving folate (methyl-tretrahydrofolate) and vitamin B-12).
Without methylation, there is no life
Produced by all living cells occurring billions of times/second in the body, SAMe serves an important biological function as a universal methyl donor (donates a methyl group (CH3) to another molecule to make it bio-active) in a multitude of cellular methylation reactions (other methyl donors include: folate, B12, TMG (Betaine), DMG and DMAE. Also, some vegetables E.g. onions, garlic, beets) contain methyl donors). SAMe functions as a donor of methyl groups in > 100 different reactions catalyzed by methlytransferase enzymes - Most cells contain numerous SAMe-dependent methyltransferases that can transfer the methyl group (CH3) to the oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur atoms of both small and large molecules. Cheng, 1999; Chang, 1996.
Affects how cells react to outside stimuli. A methyl group (CH3, a 4-atom appendage to the methione sulfur atom in SAMe) is donated to a neighbor molecule, to stimulate biochemical reactions that transform the recipient molecule into a bio-active substance. E.g. Methyl groups transferred from SAMe to certain phospholipids produce phosphatidylcholine. The presence or absence of this important lipid found in all cell membranes controls membrane accessibility to outside signals, and thus affects how cells react to outside stimuli.
Affects fetal development, brain function. Maloney, 2012; Morse, 2012
Regulates gene expression
Preserves the fatty cell membranes - the greater the amount of SAMe-produced phosphatidylcholine (via phospholipid methylation), the more fluid or less viscous the cell membrane, which may facilitate the lateral movement of proteins, such as receptors, within the lipid bilayer. Crews, 1982
SAMe serves as the methylating agent (donates methyl groups) in the synthesis of:
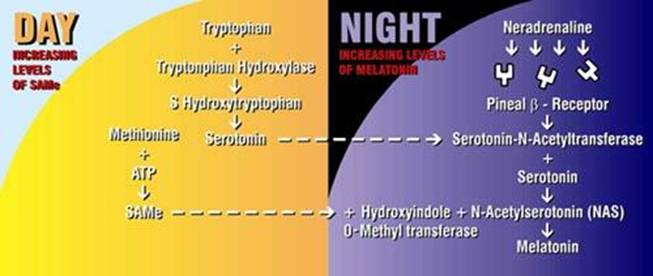
Thus, methyl donors, such as SAMe enhance sleeping, mood, energy, wellbeing, alertness, and concentration.
SAMe is the precursor for synthesis of cysteine, glutathione and taurine in the transulfuration pathway;
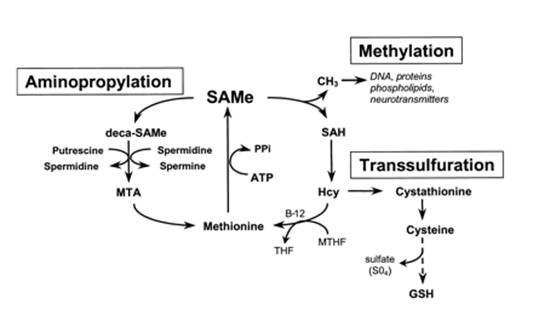
SAMe and arginine serve as precursor molecules to the aminopropylation pathway - which leads to the synthesis of polyaminesspermine, spermidine and putrescine, which are involved in the control of cell growth, gene expression, calcium homeostasis and neuron regeneration. They were also shown to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Herby, 1981; Oyanagui , 1984
This pathway, like transulfuration, also salvages and conserves methionine.
SAMe is synthesized in the body (mainly in the liver) - from methionine (an amino acid) catalyzed by the MAT enzyme (methionine S-adenosyltransferase) using ATP molecule
SAMe <=> methionine (an amino acid in protein-rich foods) - Body makes SAMe from methionine and then recycles it. Once a SAMe molecule loses its methyl group, it breaks down to form homocysteine, which is potentially toxic if it builds up within cells.
Several B vitamins (B6, B12 and folate) are required for:
(1) Transulfuration (requires B6) - Convert Homocysteine ➔ Glutathione (body's important "in-house"antioxidant);
or (2) Remethylation (requires B12, folate) - "Remethylate" homocysteine ➔ (back into) Methionine.
Sitaram BR, Sitaram M, Traut M and CB Chapman. 1995. Neurochem 65: 1887-1894.
Cheng X, Blumenthal RM. (1999) S-Adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferases: structures and functions. World Scientific Publication Co,
Chiang PK, Gordon RK, Tal J, et al. (1996) S-Adenosylmethionine and methylation. FASEB J 10:471-80. [PubMed]
Crews FT (1982) Effects of membrane fluidity on secretion and receptor stimulation. Psychopharmacol Bull. 18:135-43.[PubMed]
Levkovitz, Y., Alpert, J.E., Brintz, C.E., Mischoulon, D., Papakostas, G.I. (2011). Effects of S-adenosylmethionine augmentation of serotonin-reuptake inhibitor antidepressants on cognitive symptoms of major depressive disorder. Eur Psychiatry, 136(3), 1174-8.
Heby O. (1981) Role of polyamines in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Differentiation:19:1-20.[PubMed]
Maloney C.A., Hay S.M., Reid M.D., Duncan G., Nicol F., Sinclair K.D., Rees W.D. (2012). A methyl-deficient diet fed to rats during the pre- and peri-conception periods of development modifies the hepatic proteome in the adult offspring. Genes Nutr., Aug 21.
Morse N.L. (2012). Benefits of docosahexaenoic acid, folic acid, vitamin D and iodine on foetal and infant brain development and function following maternal supplementation during pregnancy and lactation. Nutrients, 4(7):799- 840
Oyanagui Y. (1984) Anti-inflammatory effects of polyamines in serotonin and carrageenan paw edemata—possible mechanism to increase vascular permeability inhibitory protein level which is regulated by glucocorticoids and superoxide radical. Agents Actions;14:228-37.[PubMed]
Pancheri, P., Scapicchio, P., Chiaie, R.D. (2002). A double-blind, randomized parallel-group, efficacy and safety study of intramuscular S-adenosyl-L-methionine 1,4-butanedisulphonate
Papakostas, G.I., Mischoulon, D., Shyu, I., Alpert, J.E., Fava, M. (2010). S-adenosyl methionine (SAMe) augmentation of serotonin reuptake inhibitors for antidepressant nonresponders with major depressive disorder: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Am J Psychiatry, 167(8), 942-8.