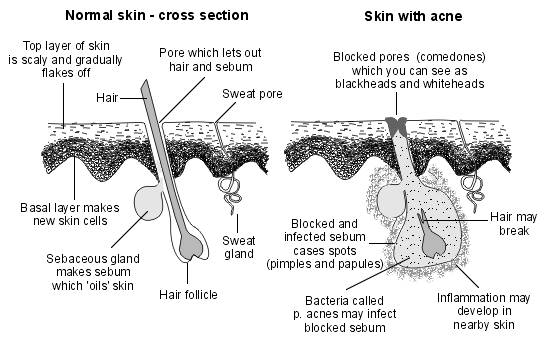
Those with acne secrete more sebum than unaffected individuals
Sebum is an oily/waxy substance secreted by the skin's sebaceous glands used to lubricate the skin and hair follicles - oddly however, the distribution of sebaceous glands and amount of sebum produced doesnot correlatewithdryskin. Sebum is composed of triglycerides, free fatty acids, wax, squalene, and a little cholesterol,with their proportions being altered in a person with acne (more squalene and TGs and less free fatty acids and wax)
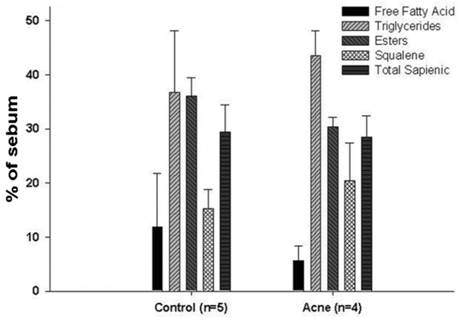
Altered Proportions of fats in Sebum of a person with acne
Overproduction of sebum can:
• Increase the incidence of clogged pores
• Stimulate inflammation- which further promotes sebum production
• Provide nutrients for bacterial growth
• Influence other factors central to the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris.
Sebum production in skin pores is increased by:
- Inflammation
- Increased male hormones. Can occur in puberty, with hyperandrogenism,low blood sugar or low blood sugar dips on a blood sugar roller coaster ride, or taking androgenic drugs.Androgen presence is only partly involved, since sebum production activity also varies with:
• Sebaceous gland receptivity to androgens. Central problem in male acne and possible role in female acne
• Sebaceous glands'ability to metabolise or synthesize (from cholesterol). Activity ofthe enzyme Type-1 5α-reductase (converts Testosterone or DHEAS to more potent DHT) is higher in sebaceous glands on the face, compared to other body areas not prone to acne.Hyperconversion of circulating androgens (called hyperandrogenism) and/or overproduction of androgens by ovaries or adrenals (called hyperandrogeny) may have roles in female acne.
• Sebaceous gland's ability to more fully use circulating androgens
- Increased INSULIN and INSULIN GROWTH FACTOR (IGF-1). Can result from high blood sugar or highs on a blood sugar roller coaster ride;
For more detail:
What Regulates Sebum Production?
Increased sebum and over-proliferation of skin cells can create a hyperkeratotic plug. Faster skin cell regeneration means more dead skin cells to be expelled, and the heavier "traffic"means they have to be clumped together for the journey out. Dead cell clumps, "glued" together with the increased sebum, invariably leads to "traffic jams" i.e. plug-blocked pores.
- These impactions contain. Corneocytes, bacteria, sebum and vellus hairs within the follicular lumen, which may or may not inflame.
- Comedogenesis begins in the lower infundibulum closely followed by kyperkeratosis of the sebaceous duct
Kligman
- High IGF-1 levels causes skin cells (keratinocytes) to multiply. Higher levels of the hormone IGF-1, which stimulates cell growth and proliferation, have been well documented as a factor in acne;