SSRI's drugs enhance brain levels of the neurotransmitter SEROTONIN, used to carry signals / pass messages between neurons (nerve cells). SEROTONIN is usually taken back into the secreting neuron from the synaptic gap between neurons, but SSRI drugs selectively block reuptake of SEROTONIN to make it more available for passing messages.
SSRI's are used to treat:
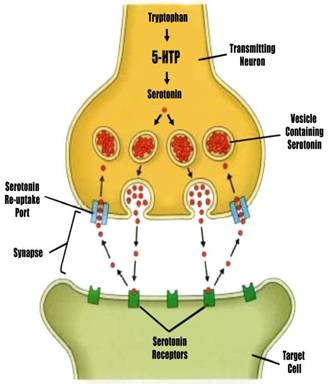
5-HTP (a seed extract of the West African plant Griffonia simplicifolia readily available OTC at reasonable cost) has been shown to produce results equal to or better than those of synthetic drugs. Used in problems arising from SEROTONIN or MELATONIN deficiency, and has been used for decades in Europe as an approved and effective treatment for a wide range of health problems, including depression, fibromyalgia, sleep problems (including insomnia), binge eating, pain, obsessive compulsive behavior, chronic headaches, weight loss, and other medical complaints.
5-HTP is the precursor to SEROTONIN - usually produced by the body from tryptophan (a food amino acid) by vitamin B3-dependent enzyme
5-HTP for SEROTONIN - Against Depression
5-HTP for SEROTONIN - Aid for Weight-loss
The body can convert SEROTONIN to the hormone MELATONIN - responsible for setting your biological clock and helping you sleep.
5-HTP for MELATONIN - Insomnia and other Sleep disorders
Tryptophan is a naturally occurring amino acid found in certain foods (especially protein) required by the human body for the production of SEROTONIN and MELATONIN.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid. Meaning it must be eaten, since the body cannot make it; L-tryptophan is also obtainable by prescription
Tryptophan Conversions |
|
| Conversions | Details |
|
Via Tryptophan hydroxylase (vitamin B3 dependent enzyme*) ▼ |
Mainly converted in intestines; B3 shortage reduces 5-HTP, SEROTONIN,MELATONIN production |
|
5-HTP |
|
|
Via 5-HTP decarboxylase (vitamin B6 dependent enzyme However, too much B6 can convert 5-HTP to SEROTONIN before it reaches the brain **) ▼ |
B6 shortage reduces SEROTONIN / MELATONIN production |
|
SEROTONIN |
Alleviates:depression, hunger, OCD's, Migraine, Fibromyalgia pain;See: SEROTONIN |
|
Via SEROTONIN n-acetyl transferase (NAT) ▼ |
|
|
N-acetyl SEROTONIN (NAS) |
|
|
Via Hydroxy-indole-O-methyltransferase (HIOMT) + SAMe (Donates a methyl group molecule to HIOMT ) SAMe -And Other Methyl Donor Molecules (vitamin B6, B12, folate dependent) ▼ |
|
|
MELATONIN |
Aids Sleep; Potent antioxidant; See: MELATONIN |
* The body often uses Tryptophan to make vitamin B3, at a very high cost of 60mg L-Tryptophan to make just 1 mg B3.
** Extremely high amounts of vitamin B6 can cause 5-HTP to convert into SEROTONIN before it reaches the brain. Consequently, this raises blood SEROTONIN levels
Conversely, however, a notable rat study found that rats with vitamin B6 deficiency produced very little SEROTONIN in the rat brain. Dakshinamurti et al, 1976
5-HTP can be taken as a supplement to increase brain's levels of the hormones:
5-HTP More easily passes blood brain barrier (BBB). For many people, getting tryptophan through the blood brain barrier is the main bottleneck leading to inadequate brain SEROTONIN levels. 5-HTP passes through the BBB into the brain far more easily than tryptophan.
Less competition / more efficient. Unlike tryptophan, 5-HTP is not used to make proteins in the body, so there is no competition for 5-HTP by cells outside the brain, as there is for the body's scarce tryptophan supplies. Human clinical studies show that 5-HTP is far more efficient at increasing brain SEROTONIN levels than L-tryptophan.
More effective against depression. 5-HTP has been a far more successful antidepressant, even when the Tryptophan dosage used is 10 to 15 times higher than the 5-HTP dosage. Also, relapses back into depression are more common with Tryptophan than with 5-HTP.
Not toxic to liver (especially when under stress). L-Tryptophan can be broken down in the liver by pyrrolase, an enzyme that converts Tryptophan to kynurenine and its metabolites, which can be mildly liver toxic at high levels. 5-HTP is not metabolized through this pathway. The stress hormone, CORTISOL, activates pyrrolase, such that any L-Tryptophan supplementation should be kept to under 1 gram (1000 mg.),especially in those who are chronically stressed.
5-HTP also increases mood /alertness neurotransmitters. Unlike Tryptophan, 5-HTP has been shown to increase brain dopamine and noradrenaline activity. These are two key mood and alertness regulating neurotransmitters, and when tyrosine, the amino-acid precursor for brain dopamine/ noradrenaline is given along with 5-HTP, the effect is even more powerful.
Dakshinamurti K, Sharma SK, Bonke D. (1990) Influence of B vitamins on binding properties of serotonin receptors in the CNS of rats. Klin Wochenschr;68:142-145.
Dakshinamurti K, LeBlancq WD, Herchl R, Havlicek V. (1976) Nonparallel changes, in brain monoamines of pyridoxine deficient growing rats. Exp Brain Res.;26:355-366.
Hartvig P, Lindner KJ, Bjurling P, Langstrom B, Tedroff J. (1995) Pyridoxine effect on synthesis rate of serotonin in the monkey brain measured with positron emission tomography. J Neural Trans ;102:91-97.