The purpose of cellular respiration is to harvest high-energy ELECTRONS from glucose, with which to produce ATP Energy. This is accomplished by a 4-step process, which oxidizes the Carbons of glucose to Carbon Dioxide and Water.
• Step 4. OXIDATIVE PHOSPORYLATION/ ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
Anaerobic cells can use this method to produce a small amount of ATP energy.
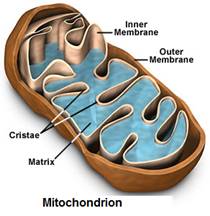
Mitochondria (Cells'"Power Plants") are large organelles with double membranes. The outer membrane is smooth, while the inner membrane has long folds called cristae.
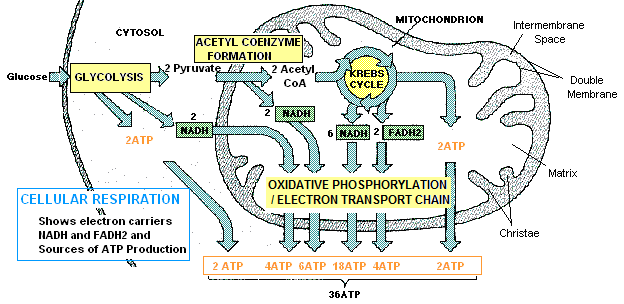
Initial removal of electrons from glucose to make two 3-carbon Pyruvate molecules
The word "Glycolysis" means to break down sugar: glyco = sugar, and lysis = to break. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryote cells. Glycolysis has 8 steps each catalyzed by a specific enzyme which nets 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH from each molecule of glucose broken down.
Glucose → 2 Pyruvate+ 2 NADH (electron carriers) + 2 ATP
After glycolysis, the pyruvate molecules enter step 2.
The next step(PYRUVIC ACID CYCLE) can also be fueled by other sources of pyruvate:
- Fatscan be oxidized to makepyruvate
- Fructose can be metabolized to pyruvate in the fructolytic pathway
Formation of Acetyl CoEnzyme A from Pyruvate
Pyruvate is shuttled into the mitochondrion where it is decarboxylated (a carbon group is removed as carbon dioxide) - and the now 2-carbon compound is attached to Co-enzyme A (CoA, a derivative of vitamin B5) forming a molecule called Acetyl CoA, stripping off another 2 electrons, which are carried by NADH.
2 Pyruvate+ CoA+ 2 NAD+ (electron acceptor) → 2 Acetyl CoA+ 2 NADH (electron carrier)+ H+ + CO2
InsufficientOxygen produces Lactic Acid - Pyruvate is turned into lactic acid instead of forming Acetyl-CoA.
Inefficient Fat Metabolism causes Brain fogging. ß-oxidation of fats supplies the best source of Acetyl-CoA, however the brain can only generate Acetyl CoA from glucose, not from fat. Aging causes fat metabolism inefficiency, causing us to burn glucose instead of fat (glucose that would otherwise have been available for the brain), to form Acetyl CoA. This explains why older people complain of brain fatigue. Acetyl CoA only lasts 2 hours in the system.
Amino acids can also be converted to Acetyl CoA for entry into the Kreb's Cycle.
Changes Acetyl CoA into Energy. Electrons are removed from Acetyl CoA forming carbon dioxide. This cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule. The Citric Acid Cycle has 8 steps each mediated by a specific enzyme. As each acetyl CoA goes around the cycle 2 carbon dioxide molecules are given off, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP. Net energy gain from Krebs per molecule of glucose is 2 ATP.
2 Acetyl CoA → 4CO2 + 6 NADH + 2 FADH2 (coenzymes carrying electrons as hydride ions + protons) + 2 ATP
(Coenzymes NAD+ & FAD* are reduced (negatively charged hydride ions added) to become electron-carrying coenzymes NADH& FADH2. A hydride ion H- is a hydrogen atom which has gained an electron. By adding this to the NAD+, the group containing nitrogen becomes neutral, forming NADH)
Electrons from the Kreb's Cycle are used to make a maximum 32 ATP molecules
The goal is to create a strong potential difference across the mitochondrial membrane, which can be used to create ATP energy - Specialized proteins and enzymes located on the inner mitochondrial membrane form a molecular "wire" (an electron transport chain). By a process called oxidative phosphorylation (the coupling of oxidation with the addition of a phosphate molecule), NADH & FADH2 donate their electrons via this "wire"(through a series of intermediate compounds)to molecular oxygen, which becomes reduced to water, producing ATP.
6 NADH &2 FADH2 →. . .. . .. . . →2 H+ and O→ H2O +32 ATP
Chemiosmosis - Hydrogen ions (protons) are used to maintain an Electrochemical Gradient that turns the electron energy into ATP. Involves pumping protons across mitochondrial membranes to establish proton gradient, which passes protons down the gradient via the enzyme ATP synthase, whereby the energy of the protons is used to generate ATP.
- When NADH & FADH2 release their electrons, hydrogen ions (H+) are also released. These positively-charged hydrogen ions are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix, using ATP energy, across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space creating an electrochemical gradient (this process is called the cytochrome oxidase system, which uses an enzyme proton pump called cytochrome oxidase acting as a step-down transformer)
- At the last stage of the respiratory chain these hydrogen ions flow back across the inner mitochondrial membrane through ion-channels - where they drive a molecular enzyme "motor"called ATP synthase in the creation of ATPfrom adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and phosphoric acid (ADP is phosphorylated into ATP), somewhat like water drives a water wheel.
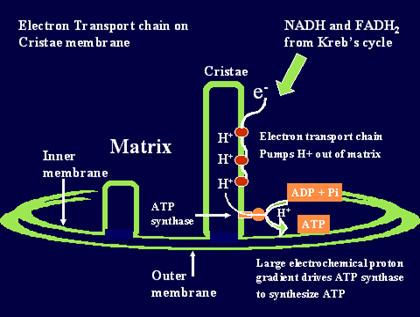
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
ATP Energy is made using the electrons that were passed down the line from glucose:
C6H12O6 (Glucose)+ 6O2 (Oxygen) → 6 CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) +6 H2O + ~36 ATP + heat
The energy released from ATP through hydrolysis (a chemical reaction with water) can then be used for biological work.