Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
The main factor determining whether or not a UTI occurs is the strength of body's defense mechanisms at the time
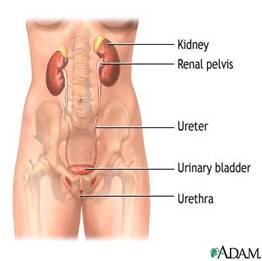
• Kidneys. A pair of purplish-brown organs located below the ribs toward the middle of the back. Kidneys remove excess liquid and wastes from the blood in the form of urine, keep a stable balance of salts and other substances in the blood, and produce a hormone that aids the formation of red blood cells
• Ureters. Narrow tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
• Bladder. A triangular shaped chamber in the lower abdomen. Urine is stored in the bladder
• Urethra. Urine in bladder is emptied through the urethra
• The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same. Except the male urethra is longer
• Urethritis. An infection limited to the urethra, where most UTIs occur;
• Bladder Infection (Cystitis). UTI spreads from urethra to the bladder;
• Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis). Untreated, sometimes the infection can travel up the ureters to infect the kidneys - a very serious condition.
• Bacterial Prostatitis. Male-only UTI causing inflammation of the prostate gland;
- Candida albicans naturally occurs in your body, but gets out of control because of antibiotics, or antibiotic chemicals (E.g. chlorine in tap water, or sodium fluoride in toothpaste)
- This yeast can invite the bad bacteria to take up residency by changing the pH of your urinary tract
- Take Grapefruit Seed Extract (GSE) or a broad spectrum herb like Wild Oregano Oil (WOO). Known to destroy yeast, viruses, bacteria etc.
a.k.a. Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS)
Interstitial Cystitis (IC) -"Painful Bladder Syndrome"
Normal urine is sterile and has a slightly acidic pH. Urine contains fluids, salts, and waste products and is normally free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi;
- Urine's only slightly acidic pH allows it to control growth of many microorganisms. The bacteria that cause most UTIs like a more acid environment, but produce alkaline waste that will eventually slow down their own growth;
- Healthy pH urine levels are 6.0 - 6.5 in the morning and 6.5 - 7.0 in the evening. The higher morning acidity is due to decreased pulmonary ventilation that causes respiratory acidosis during sleep.
- Urine pH can vary from 4.4 - 8. When the body ingests too many acid-forming foods/drinks, the acid can be buffered using alkalizing minerals, such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, sodium (borrowed from bone if not in diet). Excess acids can also be excreted via urine, however, a urine pH below 6.0 (morning) or 6.5 (evening) suggests that the body's buffering system is overwhelmed.
- Diet rich in citrus fruits, most vegetables, and legumes will alkalize the urine. A diet high in meat and cranberry juice will make the urine more acidic.
Microbial resistant properties of bladder lining, and prostate fluid (in men);
Flora maintain bacterial balance in anterior urethra (part of urethra closest to where urine comes out of body). Commonly colonized with normal flora, which usually maintains a balance with bacterial contaminants, e.g. from rectum, skin, or vulva.