In biological systems, REDOX reactions using the OXIDANT ability of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) are essential to body's functions maintaining life

When we say Oxygen "OXIDIZES" Food, What Does that Mean?
Oxygen Molecule (3 O2) "Activated" to Produce ROS by 2 Different Mechanisms
ROS production in the body can be Enzymatically or Non-enzymatically mediated
ROS are produced continuously in cells either as by-products of metabolism or deliberately as in immune system phagocytosis. They are also by-products of circulation, respiration, digestionand assimilation.
REDOX (REDuction/OXidation) REACTION - This chemical term refers to a two-way reaction in which:
Electrons are removed from glucose in a series of enzyme-assisted steps, which pass them along an "Electron Transport Chain"until they are finally accepted by oxygen, producing water. Glucose is the "reductant" in this redox reaction, since glucose "reduces"(gives away electrons to) oxygen.
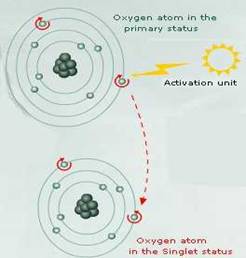
If atmospheric Oxygen (3 O2) absorbs sufficient energy to reverse the spin of one of its unpaired electronsit will form the ROS singlet oxygenin which its two unpaired electrons have opposite spins.
Singlet oxygen does not then have the spin restriction of triplet oxygen, and can thus participate in reactions involving the simultaneous transfer of two electrons (divalent reduction). Since paired electrons are common in organic molecules, singlet oxygen is much more reactive towards organic molecules than 3 O2 .
Singlet oxygen can be introduced into the body by various therapies E.g. Ozone therapy, Hydrogen peroxide therapy, PDT
(Photodynamic Therapy -provides benefit of light therapy on photosensitive molecules purposefully introduced to target areas off body)
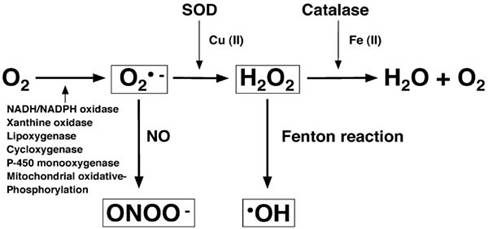
In the body, ROS are more typically produced by the progressive reductionof Oxygen to form Superoxide, Hydrogen Peroxide, Hydroxyl Radical and finally water.
The energy-producing cellular respiration chain in the mitochondria (the energy "factory" of cell)uses more than 90% of the body's oxygen, in a 4-step processthat takes place one electron-transfer at a time, ultimately producing water, carbon dioxide (CO2) and energy. The summary process of how cells produce energy from glucose in the presence of sufficient oxygen is:
C6H12O6 (glucose)+ 6 3O2→ 6 CO2 +6 H2O+ Energy
These partial equations show the intermediate ROS produced during this 4-step process:
|
1 |
3 O2+e -→O2 |
Superoxide Radical (mildly reactive) |
Adding 1e- to molecular oxygen |
|
2 |
O2• -- +H2O→HO2• +OH-- |
Hydroperoxyl Radical (highly reactive) |
Adding H to Superoxide |
|
3 |
HO2• +e-+ H →H2O2 |
Hydrogen Peroxide (poorly reactive) |
Adding 2 e- to molecular oxygen |
|
4 |
H2O2+e-→ OH•+OH-- |
Hydroxyl Radical (extremely reactive) |
Adding 1e- to Hydrogen peroxide |
A variety of enzyme systems are capable of generating significant amounts of free radicals, including:
Lipoxygenase enzymes catalyze reactions
between 3
O2
and PUFAs (polyunsaturated fatty acids), such
as arachidonic acid (AA), containing methylene
interrupted double bonds.
When AA is the substrate, these Hydroperoxides are known as HpETEs which can be
transformed into Hydroxy products (HETEs).
Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes catalyze the addition of 3O2 to various PUFAs, converting them into biologically active molecules called endoperoxides(PGG, PGH) - intermediates in the transformation of fatty acids to prostaglandins.
Myeloperoxidase -produced in neutrophils, monocytes and newly activated macrophages, catalyseshydrogen peroxide's oxidation of chloride ions into the powerful oxidant hypochlorous acid (HOCl)
Prostaglandin synthase
Aldehyde oxidase
Amino acid oxidase.
Autoxidation is a by-product of the aerobic internal milieu - molecules that undergo autoxidation include:
Catecholamines
Haemoglobin
Myoglobin (in heavily exercised muscles)
Rreduced cytochrome C
Thiol.
Autoxidation of any of the above molecules in a reaction results in the reduction of 3O2 and the formation of ROS -Superoxide is the primary radical formed.
A ferrous ion (Fe II) also, can have its electron stolen from it by oxygen to produce superoxide and Fe III - by the process of autoxidation (Fridovich, 1983 and 1995)