Certain activated IS white blood cells(WBCs / leukocytes) produce strong oxidants** to kill pathogens at infection sites, and oxidize (Eliminate toxins and abnormal cells. For Example: Phagocytes produce Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 , hydroxyl radical OH•, and ozone O3 to kill bacteria and viruses.
**Oxidants are atoms or molecules which take electrons from other molecules, in contrast to reductants which donate electrons to oxidants.
Biooxidative therapy provides active oxidants to supplement the I.S. attack forces. Similarly dealing with microbial infection (i.e. pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), Oxidizing toxins and eliminating abnormal cells
The following therapies (at appropriate doses) provide or produce physiological oxidants (mainly reactive oxygen species (ROS) ):
Chlorine dioxide therapy (CDT using MMS)
Phospholipids and lipoproteins provide integrity to cell membranes - without which the cell is unable to survive
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), such as singlet oxygen 1O2* and hydroxyl radical (OH• ) can oxidize unsaturated fatty acids comprising the phospholipid layer of bacterial and body cell membranes - referred to as lipid peroxidation, such oxidation forms hydroperoxides, which can cause irreparable damage to membranes not protected by antioxidant systems. There is also a synergistic effect with cellular-formeds
Effects include:
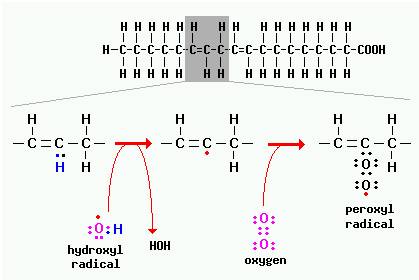
Reactions involving radicals occur in chain reactions. Note in diagram above that a hydrogen is abstracted from the fatty acid by hydroxyl radical, leaving a carbon-centered radical as part of the fatty acid. That radical then reacts with oxygen to yield the peroxy radical, which can then react with other fatty acids or proteins. (R. Bowen, Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen, Colorado State University. Link)
ROS can also directly attack membrane proteins and induce lipid-lipid, lipid-protein and protein-protein crosslinking. All affecting membrane function.
Oxygenation effect of biooxidative therapy oxidants stimulates immune system (IS) function. Allows the IS to be more effective at doing its job of removing "undesireables" from the body
Anaerobic bacteria, viruses, fungi and damaged /abnormal cells have weak or non-existent antioxidant protection systems in their membranes and thus fall prey to oxidants and are destroyed or inactivated.
"A Lightning Storm" Effect Eliminates Weak / Abnormal CellsOne way to understand the effects of oxidative therapies is to realize that at appropriately controlled concentrations, oxidants provide a "storm"that destroys weak structures, but leaves intact the strong, healthy structures that are able to withstand the onslaught.Our healthy body cells have adequate antioxidant protection against this type of "natural selection"process, whereas weak, abnormal cellsdo not, and are thus "taken out". |
Following biooxidative treatment, lactate levels decrease providing evidence that cancer cell metabolism has indeed been inhibited - due to an increased rate of anaerobic glycolysis, malignant cells produce more lactate than normal cells.
Oxidant activity and presence in the body is controlled by various means:
Normal, healthy cells have in-house antioxidant enzyme systems (supported by specific dietary trace minerals) to protect the unsaturated fatty acids in cellular membranes from damaging peroxidation - these enzyme systems: superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT),reductase and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)) that protect healthy lipid membranes from oxidation, require a sufficiency of their needed support minerals.
HOWEVER, To prevent interference with the oxidative nature of H2O2 therapy you should not take antioxidants within 2 hours of a bio-oxidative treatment.