Biooxidative therapy (sometimes called oxygen therapy) uses oxidants in LOW, CONTROLLED amounts (well below the toxic threshold) for internal, oral/dental or topical (external) therapeutic use. Note - not all biooxidative therapies are suitable for internal use.
The chemical definition of an oxidant is:
Controlled amounts of the therapy substance (E.g. O3, H2O2, ClO2) break down to form low doses of various reactive oxidants providing the driving force behind the therapy - the therapeutic radical• and non-radical oxidants produced include:
and others, depending on the actual therapy and specific reactions. Some derived oxidants are still being determined for some reactions.
Bioxidative therapy has the following beneficial effects to help treat many health problems - some of these effects are obviously only obtained when therapy is applied systemically:
|
Immune System
|
Stimulate immune function |
Oxidizes cancer cells (and other weak/abnormal cells) and inhibits tumor metabolism |
|
Oxidizes toxins, facilitating their excretion |
Oxidizes bacteria, yeast, fungi, parasites, protozoa, |
|
|
Scavenges free radicals |
Chelates heavy metals, working well with EDTA |
|
|
Deactivates viruses |
Prevents shock |
|
|
Circulation / Oxygen
|
Breaks up red blood cell clumping |
Cleans arteries and veins, improving circulation |
|
Increases cellular ATP energy production |
Increases partial pressure of oxygen in the blood |
|
|
Prevents stroke damage |
Reduces cardiac arrhythmia |
|
|
Enzymes |
Normalizes hormone and enzyme production |
Stimulates production ofcell-protective antioxidant enzymes |
|
Healing |
Reduces inflammation |
Reduces pain |
|
Stops bleeding |
Supports/enhances healing process |
|
|
Brain |
Calms the nerves |
Improves brain/memory function |
|
Disease |
Purifies the blood and lymph |
Prevents/reverses degenerative disease |
|
Prevents/Treats communicable diseases |
Prevents/Eliminates auto-immune diseases |
Health problems generally involve oxidative stress in the body's cells, meaning that Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are overwhelming cellular antioxidant systems. So when using oxidants for therapeutic purposes, logic says that we would be adding more ROS to a body in which there are already so many that they are causing problems (at present there is evidence of ROS involvement in more than 100 disease states)
ROS produced by ozone and Hydrogen Peroxide (and other biooxidative therapies) have both "Dr. Jeckyll" and "Mr. Hyde" roles. These are typically used in low, controlled amounts balanced with an antioxidant presence to attain their beneficial effects:
On the NEGATIVE side:
On the POSITIVE side:
For more detailed information, see:
Life's Oxygen Paradox - Meet Dr. ROS Jeckyll and Mr. ROS Hyde
To be an effective oxidant against health problem / disease:
Factors in dealing with pathogens:
Other weak forms of bioxidative therapy include:
Biooxidative therapy stimulates the body's production of it's "in house" enzymes which act as antioxidants, free radical scavengers and cell wall protectors :
Antioxidants are oxidant damage control
Enhanced enzyme activity is evidenced in glucose break-down (glycolysis) by an increase in:
"If your car has dirt in its oil, has half its air supply cut off, and has never had an air or gas or oil filter changed, it will die after sputtering along for a while."
- Ed McCabe - Author: "Flood Your Body with Oxygen"
| How do bio-oxidative therapies increase oxygen levels in tissues? |
|---|
|
Biooxidative therapy stimulates oxygen release from red blood cells ( RBCs) - RBC exposure to Low dose oxidants causes an increase in the their glucose breakdown (glycolysis) rate, which induces an increase in 2,3- DPG enzymes inside RBCs,which catalyze the release of oxygen into surrounding tissues. (Note: Diabetics have depressed 2,3- DPG).
|
"The microbe is nothing. The terrain is everything". This quote is ascribed to Claude Bernard (1813- 1878), and purportedly quoted by Louis Pasteur (1822- 1895) on his deathbed, thereby recanting his still taught germ theory, which assigns the cause of disease to microbes invading the body. In contrast, Bernard and Antoine Bechamp (1816- 1908) believed disease was a consequence of an imbalance in the internal terrain of the body. Basically, germs are not the root cause of disease, but rather are a sign of conditions conducive to allowing germs to flourish.
Create an inner "terrain" that is unhospitable to pathogenic microbes. So putting an end to disease- causing oxidative stress.
People are exposed to many unnatural chemicals in our environment, food and water. These overwhelm our undernourished immune system and stay in the body long enough to "gum up the works". The consequences of toxic- overload includes depleted oxygen availability , leading to clumped blood cells, sluggish circulation, and an internal environment that promotes microbial growth.
It is professionally recognized that many health problems today are caused by a lack of oxygen reaching the body's cells. Nobel Prize winner Dr. Otto Warburg announced this finding back in the 1920's.
Warburg had determined that a cancer cell had partially turned from efficient aerobic respiration to inefficient anaerobic fermentation stating in one of his lectures that ". . . the prime cause of cancer is the replacement of the respiration of oxygen in normal body cells by a fermentation of sugar".Warburg observed that mutated cells produce >50% of their energy was generated in the cytosol via inefficient glycolysis ( produces 2 ATP molecules/glucose molecule). Compare this to healthy cells, which produce >90% of their energy in the mitochondria by efficient aerobic respiration (produces~36 ATP molecules / glucose molecule).
| PET (Positron Emission Tomography) Scan | |
|---|---|
|
Cancer cells' high glucose consumption allows tumors of a certain size to be detected by a PET scan. This technique utilizes an imaging tool that picks up radio- active glucose injected into a patient. Since cancer cells produce more than half of their energy by glycolysis (break- down of glucose), they consume much more glucose than normal cells, and will therefore accumulate more radio- active material as illustrated in the picture below.
|
Today, although not accepted as a feature of carcinogenesis, it is accepted that a cancer cell has switched from oxygen respiration to fermentation, and that it is a phenomenon required by rapidly dividing cells (E.g. spermatozoa, proliferating thymocytes, intestinal mucosal cells, renal cells and embrionic stem cells.) (Wojtczak L (1996). The Crabtree effect: a new look at the old problem. Acta Biochim Pol 43,361- 368)
The mechanism for how lack of oxygen is involved in this change is still up for debate. This author holds to the microbial theory of cancer, which explains a cancer cell as one that has been invaded by a "cancer microbe", which blocks aerobic ATP energy production and eventually alters DNA in the cell nucleus to cause the cell to multiply without control. Certainly, a depleted oxygen environment would beconducive to anaerobic microbial growth and activity.
A significant body of evidence supports the theory that DNA mutations are involved with respiratory damage in cancer cells
| "The Warburg effect" (also called Aerobic Glycolysis) |
|---|
|
States that cancer cells rely on glycolysis even when oxygen becomes available. The Warburg Effect is is thought to be due to reprogramming of metabolic genes to allow cancer cells to function more like fetal cells and to enable more glucose to be used for synthesizing macromoles rather than be burned for energy. i.e. glucose is used more for replication than for normal cell metabolism. "The Crabtree Effect", attributed to Herbert G. Crabtree in 1926, found that an increase in glucose decreased oxygen uptake by tumor cells, which in contrast, induced a slight increase or no effect on respiration of normal cells. Basicially, once a cell has turned cancerous, it is not lack of oxygen keeping it there, but rather that the cell must adopt a method (i.e. fermentation) that allows increased glucose imports to meet its energy demands for multiplication. |
Increases circulation / oxygen delivery to body cells by reducing blood clumping. In circulatory disease, a clumping of red blood cells hinders blood flow through the small capillaries, increasing blood viscosity and decreasing oxygen absorption due to reduced surface area. By reducing or eliminating clumping, biooxidative therapy restores their ability to carry oxygen. Oxygenation of the tissues increases as the arterial partial pressure increases and viscosity decreases.
Additionally . . .
Biooxidative therapy enhances blood flow by:
Increases circulation by oxidizing arterial/venous plaque. Biooxidative therapy breaks down plaque inherent in both atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis(stiffening /hardening joints by fibrosis of the intima and calcification of the tunica media in the vessel wall). Ozone can clear blockages of large and small vessels, allowing for better tissue oxygenation in deficient organs.
Increases aerobic cellular ATP energy production
Certain activated IS white blood cells(WBCs / leukocytes) produce strong oxidants** to kill pathogens at infection sites, and oxidize (Eliminate toxins and abnormal cells. For Example: Phagocytes produce Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 , hydroxyl radical OH•, and ozone O3 to kill bacteria and viruses.
**Oxidants are atoms or molecules which take electrons from other molecules, in contrast to reductants which donate electrons to oxidants.
Biooxidative therapy provides active oxidants to supplement the I.S. attack forces. Similarly dealing with microbial infection (i.e. pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), Oxidizing toxins and eliminating abnormal cells
The following therapies (at appropriate doses) provide or produce physiological oxidants (mainly reactive oxygen species (ROS) ):
Chlorine dioxide therapy (CDT using MMS)
Phospholipids and lipoproteins provide integrity to cell membranes - without which the cell is unable to survive
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), such as singlet oxygen 1O2* and hydroxyl radical (OH• ) can oxidize unsaturated fatty acids comprising the phospholipid layer of bacterial and body cell membranes - referred to as lipid peroxidation, such oxidation forms hydroperoxides, which can cause irreparable damage to membranes not protected by antioxidant systems. There is also a synergistic effect with cellular-formeds
Effects include:
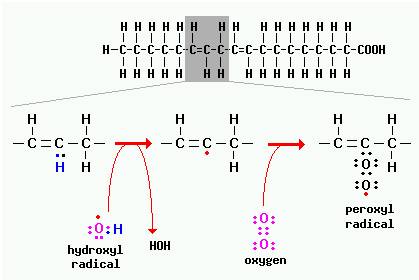
Reactions involving radicals occur in chain reactions. Note in diagram above that a hydrogen is abstracted from the fatty acid by hydroxyl radical, leaving a carbon-centered radical as part of the fatty acid. That radical then reacts with oxygen to yield the peroxy radical, which can then react with other fatty acids or proteins. (R. Bowen, Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen, Colorado State University. Link)
ROS can also directly attack membrane proteins and induce lipid-lipid, lipid-protein and protein-protein crosslinking. All affecting membrane function.
Oxygenation effect of biooxidative therapy oxidants stimulates immune system (IS) function. Allows the IS to be more effective at doing its job of removing "undesireables" from the body
Anaerobic bacteria, viruses, fungi and damaged /abnormal cells have weak or non-existent antioxidant protection systems in their membranes and thus fall prey to oxidants and are destroyed or inactivated.
"A Lightning Storm" Effect Eliminates Weak / Abnormal CellsOne way to understand the effects of oxidative therapies is to realize that at appropriately controlled concentrations, oxidants provide a "storm"that destroys weak structures, but leaves intact the strong, healthy structures that are able to withstand the onslaught.Our healthy body cells have adequate antioxidant protection against this type of "natural selection"process, whereas weak, abnormal cellsdo not, and are thus "taken out". |
Following biooxidative treatment, lactate levels decrease providing evidence that cancer cell metabolism has indeed been inhibited - due to an increased rate of anaerobic glycolysis, malignant cells produce more lactate than normal cells.
Oxidant activity and presence in the body is controlled by various means:
Normal, healthy cells have in-house antioxidant enzyme systems (supported by specific dietary trace minerals) to protect the unsaturated fatty acids in cellular membranes from damaging peroxidation - these enzyme systems: superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT),reductase and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)) that protect healthy lipid membranes from oxidation, require a sufficiency of their needed support minerals.
ALL forms of biooxidative therapy are contraindicated for people who have had a tissue or organ transplant
The body's immune system will be stimulated into attacking the transplant
At controlled oxidant doses, a biooxidative therapy stimulates the immune system (IS ). Protocols are designed to induce optimal amounts of oxidants for boosting the IS.
Detoxification by stimulating cellular immunity against infections and cancer cells
Stimulates the production of Lymphocytes and Monocytes (Types of WBCs) - Lymphocytes (T-cells, B-cells, natural killer (NK) cells)protect the body from viruses, bacteria, fungi and cancer. If deprived of oxygen, these cells malfunction by failing to eliminate invaders, and even turning against normal, healthy cells (allergic reactions). Biooxidative therapy significantly raises the oxygen levels in the blood for long periods after administration of therapy; As one result, allergies have a tendency to become desensitized.
Stimulates production of Cytokines. A family of peptide cell-to-cell signal molecules which function to regulate numerous activities of the immune system E.g. Interferon, Interleukin, Tumor Necrosis Factor:
(For a more complete list, link to the specific biooxidatiive therapy used)
| AIDS | Cystitis | Metastatic Carcinoma |
| Acne | Diabetes Type II | Migraine Headaches |
| Alcoholism | ||
| Allergies | Diabetic gangrene | Mononucleosis |
| Alzheimer's Disease | Diabetic retinopathy | Multiple Sclerosis |
| Anemia | Digestive Problems | Parasitic Infections |
| Angina | Eczema | Parkinson's Disease |
| Arrhythmia | Emphysema | Peridontal Disease |
| Arteriosclerosis | Epstein Barr | Proctitis |
| Arthritis | Food Allergies | Prostatitis |
| Asthma | Fungal Infections | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Bacterial infections | Gangrene | Shingles |
| Bronchitis | Gingivitis | Sinusitis |
| Burns | Gum Disease | Sore throat |
| Cancer | Headaches | Sores / Wounds |
| Candidiasis | Hepatitis | Temporal Arteritis |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Herpes (Simplex, Zoster) | Trichomoniasis |
| Cerebral vascular disease | HIV Infection | Ulcers |
| Cholesterol (High) | Influenze | Vascular Diseases |
| Chronic Pain | Insect Bites | Vascular Headaches |
| Cirrhosis of the liver | Leg Ulcers | Viral Infections |
| Cluster headaches | Leukemia | Warts |
| Colitis | Lupus Erythematosis | Yeast Infection |
| COPD | Lymphoma |
ALL forms of systemic biooxidative therapy are contraindicated for people who have had a tissue or organ transplant - since the body's immune system will be stimulated into attacking the transplant
A glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase deficiency makes a person overly sensitive to all types of oxidants - requiring special precautions; a biooxidative therapy decreases activity of this enzyme.
The Warburg Phenomenon and Other Metabolic Alterations of Cancer Cells