What is electromagnetic energy? |
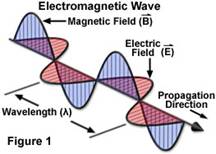
Electromagnetic fields (EMFs) are force fields having both electric and magnetic components, carrying a definite energy, and capable of producing an action at a distanceElectromagnetic radiation consists of two traveling-companion waves:(1) An electrical field (E-Field). Created by voltage (a potential difference between two points) and determines the force with which electricity is pushed through an electrical pathway (e.g. a wire, nerves, body's meridians) to produce a current. E-Field strength is measured in volts per meter (V/m). E.g. A plugged-in, unlit lamp or a charged battery has an electric field. An electric field varies with the amount of the source voltage and decreases rapidly with the distance between the two points. 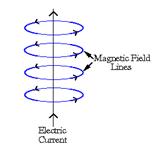
(2) A magnetic field (B-Field). A flowing electric current always produces an expanding magnetic field in addition to an electric field, with lines of force at a 90-degree angle to the direction of current flow. E.g. A lit lamp or an operating appliance has both an electric and a magnetic field. B-Field strength is measured in amperes per meter (A/m). E-Fields and B-Fields travel at right angles to each other and at right angles to the direction of wave propagation. Together they make up the total EMF. EMF strength indicates how many volts or amperes the EMF will induce in a receiving antenna that is one meter long. Currents changing direction produce EMFs which change direction at a certain FREQUENCYi.e. They vibrate / oscillate. EM waves arise as a consequence of the following two concurrent effects: (1) A changing electric field. If a current is fluctuating (vibrating), E.g. alternating Current (AC), the EM waves will fluctuate along with it. This changing field is characterized by its rate of fluctuation or vibration, called its FREQUENCY, expressed in cycles per second or Hertz (Hz.) or (2) A changing magnetic field. Induces an oscillating current in an electrical pathway, which in turn creates a changing electric field (see above). |
Natural EMFs (with nature's frequencies) are provided by the Earth, sunlight and nature. Visible light and random lightning discharges have created geomagnetic fields and electromagnetic forces since the earth was formed. Although according to Professor Bannerjee of the University of New Mexico, Earth's geomagnetic field strength is slowly declining and has lost up to half its intensity in the last 4,000 years.

UNNATURAL EMFs (using frequencies not found in nature) were first introduced when Thomas Edison built the first power station in New York City. After 100 years of using electromagnetism in technology, we now have an electromagnetic environment unlike any before. Some experts believe that the wide spectrum of artificial man-made EMF radiation masks the natural beneficial frequencies.
| Altered cell chemistry | Altered hormone levels |
| Affected calcium ion bonding in cells | Altered immune processes |
| Caused defects in chick embryos | Modified human brain waves |
| Altered behaviour of cells, tissues, organs and organisms; | Caused sterility in male animals |
"Everything in life is vibration" - Albert Einstein
"Everything in life is vibration" - Albert Einstein
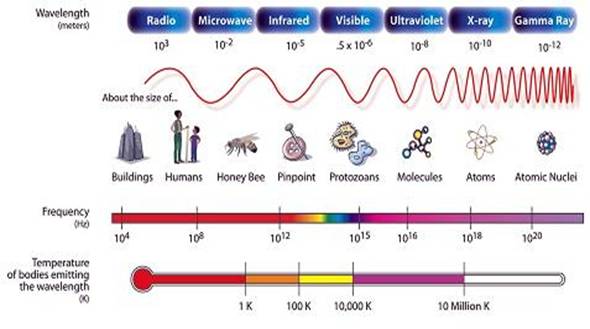
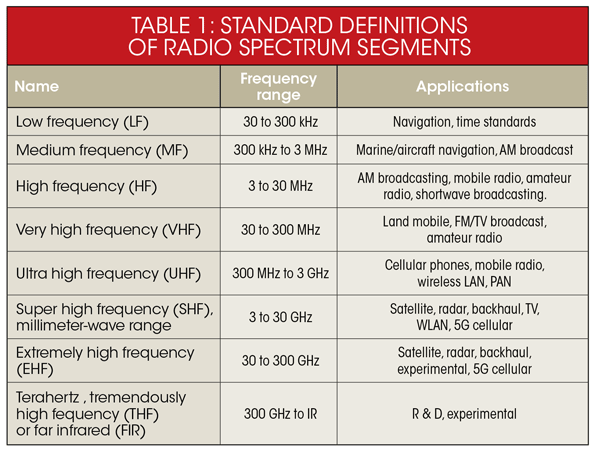
The sun radiates an electromagnetic spectrum into space over a range of frequencies - from zero frequency (a static field) to trillions of cycles per second, which electromagnetic radiation (EMFs) we have named:
The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength (the distance between one wave and the next) and the greater the amount of energy in the field
The narrow band of visible light represents 43% of the sun's total radiant energy emitted - Only the visible, radio, near infrared, and some UV electromagnetic radiation frequencies are able to reach Earth's surface from space.
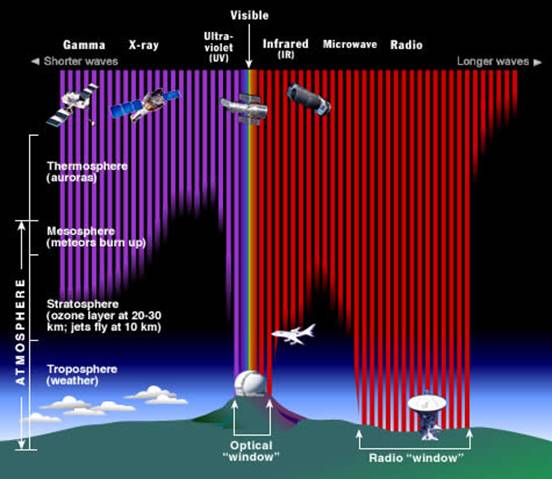
Sunlight (Sun's visible, UV and NIR frequencies (E.g. visible light has a frequency range of 430-770 THz (a tera Hertz = 1012 Hz).)
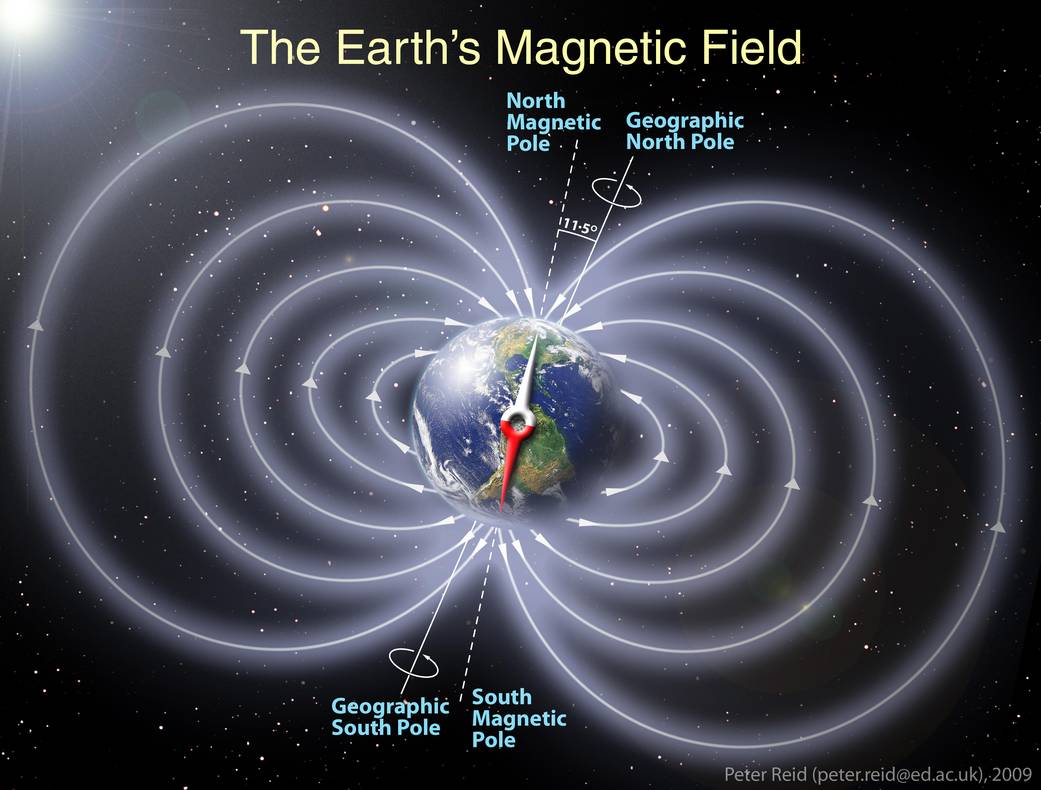
The geomagnetic field, a dipole static electromagnetic field, is considered to be mostly caused by electric currents in the liquid surrounding the earth's solid core (Not as previously thought, by the earth's spinning core of molten iron). It serves to deflect most of the solar wind, whose charged particles would otherwise strip away the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
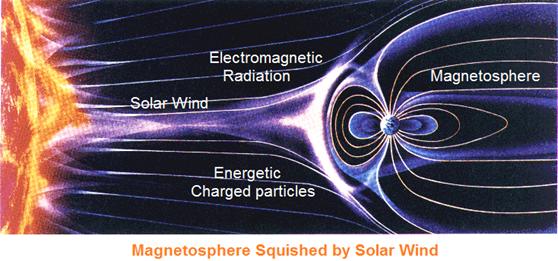
Geomagnetic field distorted by solar wind and the sun's electromagnetic radiation
The Schumann Resonances (SRs) resonate ("ring") in the cavity formed between Earth's
surface and the inner edge of the ionosphere
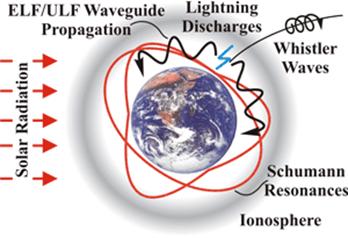
The SR frequencies can vary by geological location and are determined by the cavity size.
SRs are measured at various locations on Earth
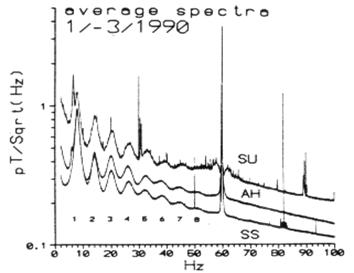
SR Data measured at Arrival Heights, Antarctica (AH), Sondrestromfjord, Greenland (SS), and Stanford, California (SU)
"Everything in life is vibration" - Albert Einstein
Mostly due to low-frequency oscillating EMFs from thunderstorms. With most effect from equatorial zones of Central Africa and the Amazon basin
To a lesser degree:
A Negative Oxygen Ion carries energy as an EXTRA ELECTRON which has bonded to an Oxygen molecule or atom. Sufficient energy acting upon a molecule, such as carbon dioxide, water, oxygen or nitrogen, can knock an electron away from that molecule. The displaced electron then attaches to a nearby oxygen molecule forming a negatively-charged oxygen ion ( NOI).
Water, water everywhere, but not a lot for us. Only 3% of Earth's water is fresh water, of which 2% is frozen in icecaps and much of the remaining 1% is inaccessible, deep in the Earth. 98% of what is left is used in industry and agriculture, leaving the rest for every living organism. (The human body is ~70% water and sap is ~90%).
Water can carry energy necessary for our health. Natural energy (e.g. the geomagnetic field, sunlight) can be transferred to water, causing its molecules to take an orderly, crystal-like form, which can change shape. Thus, information from a natural energy source can be held in the crystal's structure. Water from a deep well or a bubbling mountain stream, or distilled water (empty of energy) exposed to positive thoughts (such as love and gratitude), prayer or soothing music contains structure. Dr. Masaru Emoto, a Japanese researcher and author of "The Message from Water", captured the images of water shown here using a device called a magnetic resonance analyzer.Dr. David Schweitzer, grandson of Albert Schweitzer, was the first scientist to photograph the effects of thoughts, captured in water.
(Note: the water used in these pictures was frozen before taking the pictures)


| WATER MEMORY TRANSFER |
|---|
The theory of water memory transfer was established by the late Dr. Linus Pauling, who won the Nobel Prize for Biochemistry. In 1999 scientists at the European Union Physics laboratory in Francewere able to prove that water transfers memory via covalent bonding. |
(The brain is 85%, blood is 90%, muscles are 75%, the liver is 82%, even our bones are 22% water)
On the down-side, unnatural or negative energy can cause water to lose its structure. For example, when water is polluted or chemically treated, exposed to negative emotions, or heavy metal rock music.
Experiments by Dr. Emoto. Samples of water were collected from different areas of the world. Water from each location was divided and placed into petri dishes. Various words were written and taped to the samples. The samples were then frozen, and viewed through a microscope at magnifications of 200-500X. Results were fully repeatable.

"Water behaves more like a sensitive animal rather than an inconsequential fluid."
- Dr. Emoto
There are several devices on the market for producing EMFs with specific beneficial frequencies for therapeutic purposes - including:
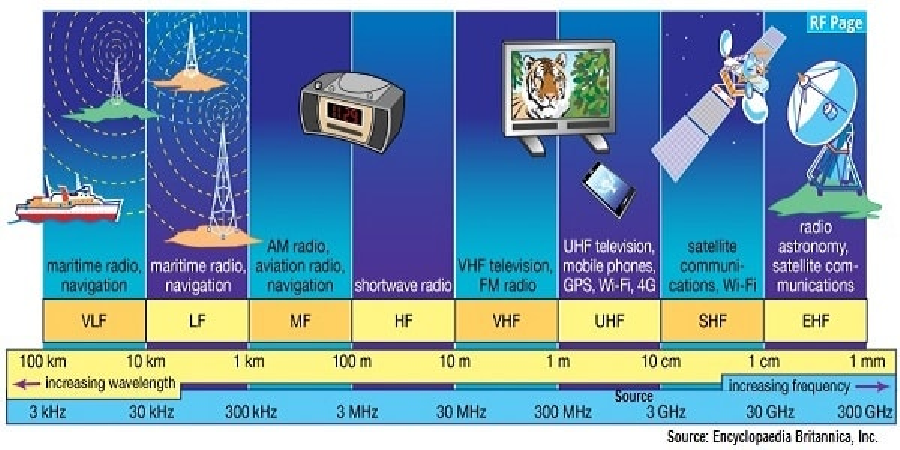
Man-made electromagnetic fields are generally divided into two groups according to their frequency level:
Extremely-Low Frequency (ELF) Range. According to generally accepted usage, the ELF region is from ~3 Hz to 300 Hz. ELF EMFs are produced by alternating current flowing in power grids:
ELF fields are produced in power lines, electrical wiring, and electrical equipment. E.g.high power transmission lines, transformers, computers, monitors, fluorescent lights, televisions, hair dryers, and digital alarm clocks.

Many pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) therapy devices also use ELF frequencies. Whether they are beneficial or not depends on the actual frequency being utilized. Some ELF frequencies are naturally used by our body to maintain health. E.g. the brain operates on different ELF ranges throughout the day called alpha, beta, alpha, theta and delta waves.

EMF penetration of earth and oceans increases as frequency decreases. At 5MHz the penetration is about 0.12 m. However, at 5Hz, the penetration is 112m. Thus, ELF/ULF EMF waves (5-50Hz) penetrate deep into the earth and oceans, and are used for submarine communications (U.S. 77 Hz, Russia 83 Hz).
ELFs are not necessarily harmless and may be "Wolves in Sheep's Clothing". Since these widespread EMF frequencies are so low and do not demonstrate any dramatic thermal or ionizing effects (as produced by nuclear devices), there has been a commonly held fallacy that they must therefore be harmless, however: