"The Body Electric"
- I Cor. 12:12a
A multicellular organism requires coherent and coordinated communication between its cells to be able to synchronize cellular processes. In living organisms, information is carried between cells via two systems:
Mainly cells sending CHEMICAL signals. E.g. hormones, neurotransmitters, hormonal growth stimulants / inhibitors, cytokines, immune system signals.
Neurotransmitters are secreted across the gap between neurons (called the synapse) to trigger receiving neurons to transmit their specific message from the neuron's receiving dendrites to its sending axon terminals. It does this by creating a so called "action potential" - an electrical pulse which travels the length of the neuron - like a current down a wire.
Almost all the body's components are linked together: a NUCLEAR matrix within an INTERCELLULAR matrix within an EXTRACELLULAR connective tissue matrix
The nuclear matrix is a network of fibers in the nucleus. These fibers link the cell's genetic components in the nucleus to the nuclear membrane.
The intercellular matrix (or Cytoskeleton) is the cell's scaffold. It transmits electrical messages inside cells from the cell membrane to the organelles, continuing through the nuclear membrane to make contact with the chromosomes.
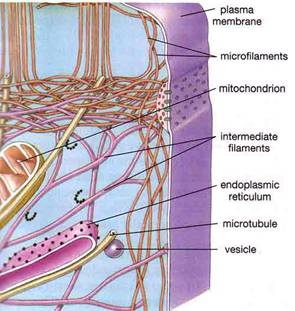
The cytoskeleton organizes and maintains the cell's shape and anchors organelles and enzymes in place. The cell interior (the cytoplasm) is virtually filled with fibers, tubes and filaments, collectively called the intercellular matrix.
The intercellular matrix has 3 types of struts:
These continuous connections link the cell membrane to the organelles - including a connection through the nuclear membrane to the chromosomes.
The enzymes of the cell are attached to this cytoskeleton
| Vibrational Therapies Can "Do the Talking" |
|---|
|
Scientists now realize that cell membrane receptors also function as antennae able to pick-up specific energy frequencies. Using the body's electrical matrix, each and every cell (and their components) are able to convey and receive vibratory information to and from other cells. Energy therapies are able to restore and reinforce this vibratory circuitry, which may be impaired by physical and/or emotional trauma and cause the immune system repair systems to falter. |
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a network of body tissue "cables" lying outside the cells. The existence of an extracellular communication network is only more recently gaining recognition in Western medical understanding, some even referring to it as an unrecognized organ
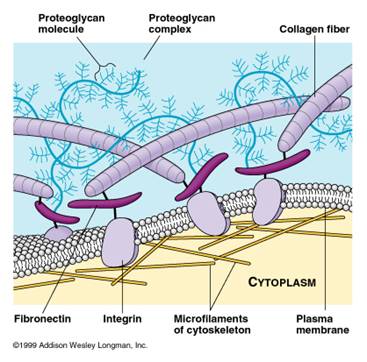
ECM connects to Intercellular Matrix via Protein Polymers
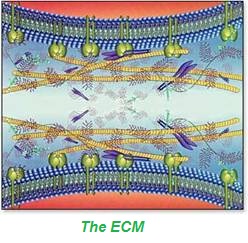
Information is carried through the ECM by very weak electromagnetic fields via their frequency and amplitude fluctuations. The Chinese have known of this network for about 5,000 years, calling the energy which travels along it our life-force or Chi (Qi). In 1994, this network (also called a meridian system) was able to be mapped accurately using high-tech instruments now available, capable of measuring minute amounts of electricity.
Where is the ECM? Situated between the cell membranes and the nearby nutrient-carrying blood vessels, the ECM is a network of connective tissue, which provides strength, fills spaces between cells, binds cells and tissues together and links almost every cell in the body.
ECM is plentiful in various connective tissues. Tendons, dermis (tough/flexible), bone (hard/dense), cartilage (resilient), jelly in eye interior (soft/transparent).
The ECM consists mostly of:
LAMININ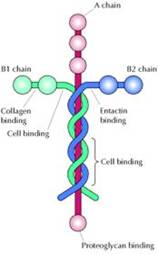 Laminin (also called the "basement membrane") is a "Cross-shaped" cell ADHESION protein molecule that holds our body together Laminin anchors organs to itself, forming sheets of protein that form the substrate of all internal organs. It has 4 arms in the shape of a cross - the three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, which is what enables it to form sheets. The long arm is capable of binding to cells, which helps anchor the actual organs to the membrane. He (Christ) is before all things and IN HIM ALL THINGS HOLD TOGETHER." - Colossians 1:17 |
Embedded in the glycoprotein gel are various protein polymers
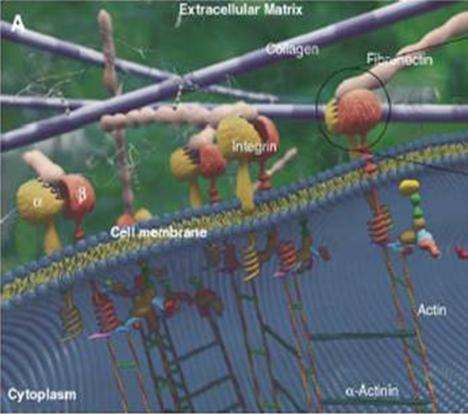
Protein Polymers
The ECM acts as a molecular sieve between the capillaries (smallest of the blood vessels) and the cells. Substances are diffused between capillaries and ECM. E.g. Oxygen is transferred from capillaries to ECM and carbon dioxide is transferred from ECM to capillaries.
The ECM is a transit and storage area for nutrients, water and waste
Edema toxifies the ECM
Cell Growth Control. ECM is involved in regulating cell growth control.
Details on the Matrix Connections
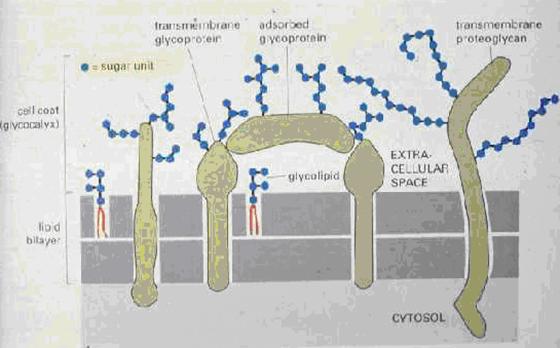
Glycocalyx:
Oligosaccharide side chains attached to membrane glycolipids and glycoproteins
The glycocalyx. Composed of negatively charged sialic acid molecules that cap the tips of glycoproteins and glycolipids that extend outward from the cell membrane like tree branches.