Evidence suggests an immuno-enhancing function for MELATONIN - stimulation of natural killer cell activity, cytokine expression and inhibition of immune cell apoptosis have been reported.
Guerrero JM, Reiter RJ. MELATONIN-immune system relationships. Curr Top Med Chem 2002;2:167-79.
Withyachumnarnkul B, Nonaka KO, Santana C, et al. Interferon-gamma modulates MELATONIN production in rat pineal glands in organ culture. J Interferon Res 1990;10:403-11.
Animal research has shown that inhibition of MELATONIN synthesis weakens cell-mediated immunity (acquired immunity where T lymphocytes have predominant role) and humoral immunity (immune response, mainly against bacterial invasion, mediated by B cells).
Pandi-Perumal SR, Srinivasan V, Maestroni GJ, Cardinali DP, Poeggeler B, Hardeland R. MELATONIN: Nature's most versatile biological signal? FEBS J. 2006 Jul;273(13):2813-38. PubMed
MELATONIN increases production of interleukin 2 and 6 (IL-2 and IL-6). MELATONIN receptors are found in lymphatic tissue, which supports the premise that MELATONIN has a direct regulating effect on the immune system. A study evaluating IL-6 during nocturnal sleep,sleep deprivation and different sleep stages concluded that:
"Loss of sleep may serve to decrease nocturnal IL-6 levels, with effects on the integrity of immune system functioning. Alternatively, given the association between sleep stages and IL-6 levels, depressed or aged populations who show increased amounts of REM sleep and a relative loss of slow wave sleep may have elevated nocturnal concentrations of IL-6 with implications for inflammatory disease risk."
Laura Redwine, Richard L. Hauger, J. Christian Gillin and Michael Irwin. Effects of Sleep and Sleep Deprivation on Interleukin-6, Growth Hormone, Cortisol, and MELATONIN Levels in Humans. Home Archive Oct 2000 85 (10): 3597 JCEM
MELATONIN helps protect the body from cell damage caused by free radicals:
Kilic E, Özdemir YG, Bolay H, Kelestimur H, Dalkara I. Pinealectomy aggravates and melatonin administration attenuates brain damage in focal ischemia. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab 19:511-516, 1999.Medline
Baydas, G., H. Canatan and A. Turkoglu, 2002. Comparative analysis of the protective effects of melatonin and vitamin E on streptozocin induced diabetes mellitus. J. Pineal Res., 32: 225-230.PubMed
Beckman J.S., Koppenol W.H. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: The good, the bad and ugly// Am. J. Physiol.-1996
Bone health. Bone resorption is a process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals. MELATONIN has been shown to inhibit bone resorption and increase bone mass through its ability to down-regulate activation of osteoclasts.
Pandi-Perumal SR, Srinivasan V, Maestroni GJ, Cardinali DP, Poeggeler B, Hardeland R. MELATONIN: Nature's most versatile biological signal? FEBS J. 2006 Jul;273(13):2813-38. PubMed
An adequate amount of ESTRADIOL is also needed for MELATONIN to benefit bone (a salivary ESTRADIOL test may be useful in cases where MELATONIN is low and bone loss is a concern).High CORTISOL levels also contribute to bone loss.
Raff H, Raff JL, Duthie EH, Wilson CR, Sasse EA, Rudman I, Mattson D. Elevated salivary cortisol in the evening in healthy elderly men and women: correlation with bone mineral density. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999 Sep;54(9):M479-83. PubMed
At present, the validity of MELATONIN as an oncostatic agent seems well established. The antitumor mechanisms of MELATONIN have been identified, including:
Circulating levels of MELATONIN are depressed in a wide variety of cancers. Including breast, endometrial, prostate, lung, gastric and colon.
Bartsch C, Bartsch H.MELATONIN in cancer patients and in tumor-bearing animals. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;467:247-64. PubMed
There are, however, isolated reports of tumor growth stimulation, especially if MELATONIN is administered in the morning. Indicating a circadian-stage dependency of antitumor action.
Bartsch H, Bartsch C. Effect of MELATONIN on experimental tumors under different photoperiods and times of administration. J Neural Transm 1981;52:269-79.
A recent controlled trial shows the possibility to improve chemotherapy - in terms of both survival and quality of life of patients with advanced disease by a concomitant administration of MELATONIN and cisplatinium etoposide in metastatic non small cell lung cancer.
Lissoni P, Chilelli M, Villa S, et al. Five years survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy and MELATONIN:
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer risk was increased among subjects who frequently did not sleep during the period of the night when MELATONIN levels are typically at their highest. There was also an indication of increased risk among subjects with the brightest bedrooms. Graveyard shiftwork was associated with increased breast cancer risk. Night shift work, Light at night, and Risk of breast cancer
Breast Cancer research clearly shows solid links between low late-night MELATONINand increased breastcancer cell growth. A study demonstrated that MELATONIN-rich blood suppressed the growth of human breast cancer xenografts and rat hepatomas. No growth suppression occurred in tumors perfused with MELATONIN-deficient blood collected from the same women after short-term ocular exposure to bright light at night.
Blask DE et al. MELATONIN-depleted blood from premenopausal women exposed to light at night stimulates growth of human breast cancer xenografts in nude rats. Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;65(23):11174-84. Pub Med
Sandra E. Sephton, Robert M. Sapolsky, Helena C. Kraemer, David SpiegelDiurnal Cortisol Rhythm as a Predictor of Breast Cancer Survival. Oxford Journals MedicineJNCI Volume92, Issue12 Pp. 994-1000 JNCI
Reduced MELATONIN production has been proposed as a likely factor in the significantly higher cancer rates in night workers. In 2007, The World Health Organization cited late night shift work as a probable cancer-causing agent. When someone works in artificial light, they generally have lower MELATONIN, and without this antioxidant and suppressant of tumor development, they may be more likely to develop cancer.
Straif, Kurt; Baan, Robert; Grosse, Yann; Secretan, BéAtrice; Ghissassi, Fatiha El; Bouvard, VéRonique; Altieri, Andrea; Benbrahim-Tallaa, Lamia et al. (2007). "Carcinogenicity of shift-work, painting, and fire-fighting". The Lancet Oncology 8(12): 1065-6.
Lower nocturnal MELATONIN levels are associated withlarger tumors in patients with primary prostate cancer
Vijayalaxmi, Charles R. Thomas, Jr, Russel J. Reiter, Terence S. Herman. MELATONIN: From Basic Research to Cancer Treatment Clinics.Journal of Clinical Oncology, Vol 20, Issue 10 (May), 2002: 2575-2601JOCO
Endogenous MELATONIN stimulates anti-cancer defenses and exhibits anti-proliferative and antioxidant activity
Claustrat B, Brun J, Chazot G. The basic physiology and pathophysiology of MELATONIN.Sleep Med Rev. 2005 Feb;9(1):11-24. PubMed
MELATONIN is produced by enterochromaffin cells of the GI mucosa and discharged into the gut lumen. Where, produced in amounts many times greater than the pineal gland, MELATONIN has several surprising roles protecting the GI tract from damage and preventing forms of gastritis.
Konturek SJ, Zayachkivska O, Havryluk XO, Brzozowski T, Sliwowski Z, Pawlik M, Konturek PC, Cze?nikiewicz-Guzik M, Gzhegotsky MR, Pawlik WW.Protective influence of MELATONIN against acute esophageal lesions involves prostaglandins, nitric oxide and sensory nerves. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;58(2):361-77.[PubMed]
Jaworek J, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ. MELATONIN as an organoprotector in the stomach and the pancreas. J Pineal Res. 2005;38:73-83. [PubMed]
Thor PJ, Krolczyk G, Gil K, Zurowski D, Nowak L. MELATONIN and serotonin effects on gastrointestinal motility. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007;58 Suppl 6:97-103. [PubMed]
Konturek PC, Konturek SJ, Hahn EG. Duodenal alkaline secretion: its mechanisms and role in mucosal protection against gastric acid. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:505-512. [PubMed]
de Souza Pereira R. Regression of an esophageal ulcer using a dietary supplement containing MELATONIN. J Pineal Res. 2006;40:355-356. [PubMed]
Pereira Rde S. Regression of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms using dietary supplementation with MELATONIN, vitamins and aminoacids: comparison with omeprazole. J Pineal Res. 2006;41:195-200. [PubMed]
Zimmermann RC, McDougle CJ, Schumacher M, Olcese J, Mason JW, Heninger GR, Price LH. Effects of acute tryptophan depletion on nocturnal MELATONIN secretion in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993;76:1160-1164. [PubMed]
Jaworek J, Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ. MELATONIN as an organoprotector in the stomach and the pancreas. J Pineal Res. 2005 Mar;38(2):73-83.
Damage-protective mechanisms of pancreas and GI tract. MELATONIN prevents various forms of gastritis and pancreatitis, via:
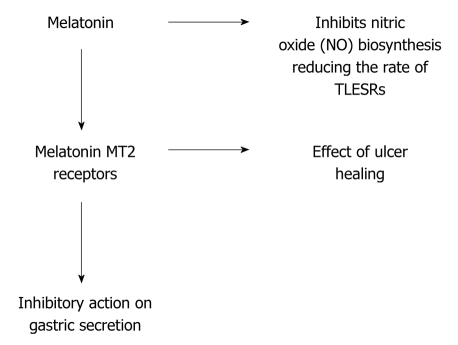
- Activation of specific MT2-receptors
- Scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS) -MELATONIN counteracts the increase in the ROS-induced lipid peroxidation and is partly responsible for preserving the activity of key anti-oxidizing enzymes such as superoxide dismutase(SOD)
Accelerates the healing of chronic gastric ulcerations
- By stimulating the microcirculation
- Interacting withinflammation-controlling prostaglandins, nitric oxide released from vascular endothelium, and/or sensory nerves and with their neuropeptides.