Sweeteners

Nutritive sweeteners provide a sweet taste and a source of calories or energy, whereas NON-nutritive sweeteners are sweet without the usual calories
NNS are low calorie sweetener alternatives added to many drinks and food products. In the U.S., the FDA permits food labelling as follows:
There are 3 types of NNS: Plant-derived (e.g. stevia, allulose), sugar alcohols (e.g. erythritol, xylitol), and artificial (e.g. aspartame, sucralose, saccharin)
NNS use is growing rapidly. The 2009-2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) suggests that 2009-2012 NNS adult consumption has doubled and child consumption has increased 54% since 1999-2000. (Sylvetsky et al, 2017; NHANES 2009-2012).
NNS were introduced with the intention of reducing caloric intake and controlling blood glucose levels without compromising the human desire for the taste of sweet. However, as consumption of non-nutritive artificial sweeteners (NAS) has increased, the percentage of the population with a high BMI has continued to rise:
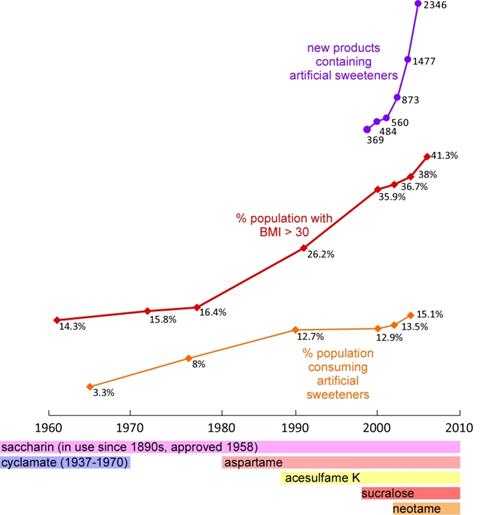
Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 January; 89(1): 1-14.
Artificial NNS cause weight gain
Non-nutritive artificial sweeteners (NAS) are toxic to gut bacteria increasing risk of prediabetes
NAS have also been identified as emerging environmental pollutants. Concerning concentration levels of ace-k and sucralose have been measured in receiving waters (i.e., surface waters, groundwater aquifers and drinking waters). Such concentrations are among the highest known trace pollutants from human activity. NAS are resistant to wastewater treatment processes and so accumulate through water treatment cycles. Molecules, 2018
There are 4.2 grams in 1 LEVEL teaspoon of sugar, nutrition facts generally round this down to 4 g / tsp.
G.I. = Glycemic Index S.I. = Sweetness index (table sugar is 1) H.S. = Heat stable
| Chart of Non-Nutritive Sweeteners
(NNS) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Natural (Plant) NNS |
||||||
| Chemical name | G.I. | Cals. /tsp. |
S.I. | Plant or Trade name | Heat Stable |
Notes |
| Allulose a.k.a. D-psicose (monosaccharide with same formiula as fructose) |
0 | 1 | 0.70 | Dolcia Prima; Used like sugar 1/10 calories of sugar. Net carbs of zero calories after metabolism; FDA-approved April 2019. |
Yes | "Rare sugar" found in trace amounts in a few foods (incl. figs,
raisins, kiwi, wheat); negligibly raises blood sugar or INSULIN |
| Stevia leaf | 0 | 0 | 300 | Various foods and beverages | Yes | Distinctive aftertaste; |
| Steviol glycosides: |
0 | 0 | Stevia; Equal
naturals®; Truvia®(by Coca Cola); Stevia in the Raw®; SweetLeaf®; Sweet Drops™; Sun Crystals®; and PureVia®(by Pepsi) FDA-approved 2008; |
Yes | Leaf extracts; Licorice aftertaste |
|
| Stevioside | 300 |
|||||
| Rebaudioside A | 450 |
|||||
| Mogroside V | 0 | 0 | 150 -400 200 |
Luo Han Guo ("Monk
fruit"); Purefruit®; Nectresse®* Available as powder (mixed with bulking agents, such as dextrose or erythritol), granules, or liquid; FDA-approved 2010; |
Yes | Fruit extract; Chinese fruit; Fruity / licorice aftertaste |
| Glycyrrhizin | 0 | 0 | 50 | Licorice. | Licorice root extract; licorice flavor; inhibits enzyme that deactivates CORTISOL |
|
Sugar Alcohol NNS |
||||||
| Chemical name | G.I. | Cals. /tsp |
S.I. | Plant or Trade name | Heat Stable |
Notes |
| Erythritol (0.2
cals/g) ‎E968 |
1 | 1 | 0.7 | Equal naturals® | Yes | Produced by fermenting glucose in cornstarch |
| Xylitol (2.4 cals/g) | 7-12 | 10 | .95 -1 |
|||
| Glycerol (glycerin) |
3 | 40 | 0.4-0.8 | |||
| Sorbitol (2.6 cals/g) | 4 | 19 | 0.5-0.6 | |||
| Mannitol (1.6 cal/g) |
2 | 13 | 0.5 | |||
Artificial Sweetener NNS |
||||||
| Chemical name | G.I. | Cals. /tsp |
S.I. | Plant or Trade name | Heat Stable |
Notes |
|
Aspartame
- "Neurotoxin" "Blue packet" |
0 | 0 | 100-220 180 |
 Equal
original®; Canderel®; Nutrasweet®;Spoonful®; Equal
original®; Canderel®; Nutrasweet®;Spoonful®;Natrtaste blue®; beverages, cereals, yogurt, frozen and gelatin desserts, candy, sugar-free gum, juices, diet sodas, vitamin supplements, laxatives. |
? | Toxic to gut bacteria; Fully metabolized (50% phenylalanine, 10% methanol, 40% aspartic acid); Bitter aftertaste; |
|
Sucralose
- "Organochlorine" "Yellow packet" |
0 | 0 | 500- 755 600 |
 Splenda®;
Equal sucralose®;Zerocal®; Sukrana®; SucraPlus®; Candys®; Splenda®;
Equal sucralose®;Zerocal®; Sukrana®; SucraPlus®; Candys®;Cukren®; Nevella®; |
Yes | Toxic to gut bacteria; sourced from sucrose; |
| Saccharin "Pink packet" |
0 | 0 | 200-400 |
 Sweet
'N Low®, Sweet Twin®, Sugar Twin®, Sweet
'N Low®, Sweet Twin®, Sugar Twin®,Necta Sweet® |
Yes | Toxic to gut bacteria; Oldest artificial sweetener (1879) Familiar saccharin taste. |
| Acesulfame K (Ace K) C4H4KNO4S E950 |
0 | 0 | 200 | Sunett®and Sweet One®ACE®, ACE K®, Sweet 'N Safe®Equal original® Often in sugar-free sodas; |
Yes | Toxic to gut bacteria; Potassium salt of 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide. Bitter |
| Neotame | 0 | 0 | 10,000 7-13,000 |
Newtame® In low-calorie foods / beverages Approved 2002; |
Yes | Toxic to gut bacteria; Made by Nutrasweet; Degrades in some liquids depends on pH |
| Cyclamate | 0 | 0 | 40 | Discovered 1937; US banned it in 1969 after reports of tumors in rats ; popular approved sweetener in other countries. | ||
| Advantame | 0 | 0 | 20,000 | Yes | ||
*Nectress is manufactured by McNeil Nutritionals, the makers of Splenda®. It is mainly monk fruit extract with a small amount of erythritol (a sugar alcohol), sugar and molasses.
Equal original: Dextrose with Maltodextrin, Aspartame, Acesulfame K
Equal sucralose: Dextrose with maltodextrin, sucralose
Equal naturals: Erythritol, Stevia Leaf Extract, Natural Flavors
Nutrasweet: dextrose with maltodextrin, aspartame
Purevia and Truvia: Reb A and erythritol as granules
NHANES 2009-2012. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sylvetsky, A.C.; Jin, Y.; Clark, E.J.; Welsh, J.A.; Rother, K.I.; Talegawkar (2017) S.A. Consumption of Low-Calorie Sweeteners among Children and Adults in the United States. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 117, 441-448. PubMed