Circulating TESTOSTERONE provides the precursor for conversion to DHT and ESTRADIOL
In tissues containing 5a-Reductase (5AR) enzyme- ~7% of TESTOSTERONE is converted to the more potent androgen DHT, which activates the AR leading to a 2-3 times stronger androgenic response than TESTOSTERONE;
• Androgen target tissues include skin and prostate
In tissues NOT containing 5AR
- TESTOSTERONE initiates a direct androgenic response when binding to the androgen receptor (AR) - by inducing expression of androgen-dependent genes;
• Major metabolites of DHT are 3B-androstenediol and 3B-androstenediol -these are conjugated to glucuronic acid in the liver for renal excretion
In tissues containing aromatase - TESTOSTERONE converts to ESTRADIOL (and ANDROSTENEDIONE converts to ESTRONE in females) in estrogen - responsive tissues (i.e. those containing Estrogen Receptors (ER's)), including skin and liver. This may:
(1) Exert an effect in situ if tissue is estrogen-responsive
Or (2) Enter plasma for distribution to peripheral target tissues - mainly adipose tissue (in men or women)
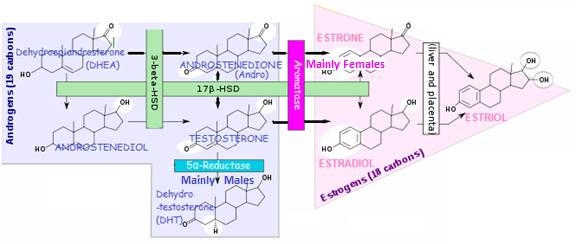
• DihydroTESTOSTERONE (DHT) - in testes, liver, brain, prostate, external genitalia, skin, hair follicles and sebaceous glands (via 5AR enzyme);
• ESTRADIOL - in testes (~ 1/3 of male circulating ESTRADIOL), ovaries, liver, fat, muscle, brain (via aromatase enzyme; male levels of estrogen tend to increase with age (at the expense of TESTOSTERONE) due to increased aromatase activity;
• ANDROSTERONE - a weak androgen, ~1/7 potency of TESTOSTERONE
• ANDROSTANEDIOLS
• Glucuronide - in liver for renal elimination
• Etiocholonolone