The conversion of one hormone to another is catalyzed by a certain enzyme. As depicted in the rectangular boxes in the following steroid conversion chart.
The level of an enzyme presence in a particular body tissue determines the extent to which the hormone conversion will take place. The amount of a certain hormone in particular areas is a critical factor affecting hormonally related health concerns.
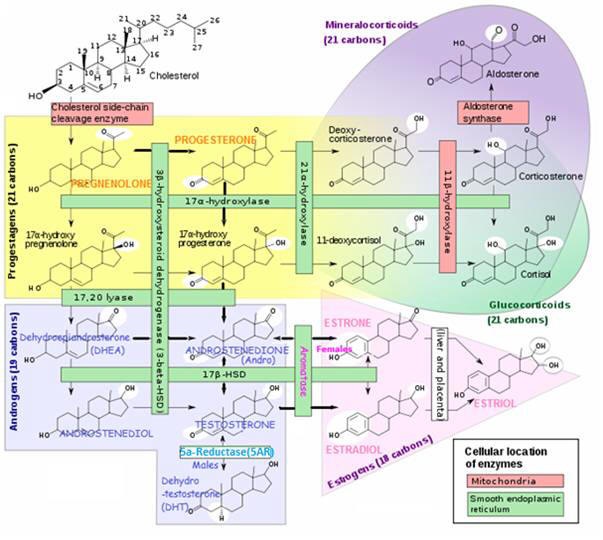
Steroid conversion chart
(conversion enzymes are shown in rectangular boxes)
At a Glance ChartEnzymes affecting Steroid Production/Activity and Conversion Pathways |
||||
|
Enzyme |
Converts |
Prod'n / Activity Conversion Pathway Increased by: |
Prod'n / Activity Conversion Pathway Decreased by |
Comments |
|
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme; |
Cholesterol âž” PREGNENOLONE (in mitochondria); |
LH |
Estrogens; Lead; Vitamin A deficiency; Certain drugs |
Series of reactions occur at the inner membrane; |
|
(17α-hydroxylase) |
LH |
TESTOSTERONE (affects cAMP pathway) Ethanol; Nicotine; Certain drugs |
Catalyzes hydroxylation and cleavage (converts steroids from a 21-carbon to a 19-carbon molecule in Δ4 and Δ5- hydroxysteroid pathways); |
|
|
(17ß-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase) |
DHEA âž” ANDROSTENEDIOL ANDROSTENEDIONE ⇔ TESTOSTERONE ESTRONE (E1) âž” ESTRADIOL (E2) |
Drugs: Cotinine, Danazol, Cyclosporin A, Lithium chloride. Lignans (E.g. in flaxseed) |
Lignans - Enterolactones (lignan precursors) found in E.g.flaxseed inhibit |
|
|
(3ß-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase) |
PREGNENOLONE âž” PROGESTERONE DHEA âž” ANDROSTENEDIONE |
LH FSH via LH |
TESTOSTERONE Lead; Daidzein /genistein /biochanin A (isoflavones), Aflatoxin |
In the male, FSH, stimulates release of a Sertoli cell factor that increasesLH effect on 3ß-HSD activity; |
|
TESTOSTERONEâž” DIHYDRO-TESTOSTERONE (DHT) |
In testes, liver, brain, prostate, external genitalia, skin, hair follicles and sebaceous glands; DHT more potent than TESTOSTERONE; DHT involved in BPH,prostate cancer, hirsutism |
|||
|
TESTOSTERONE âž” ESTRADIOL ANDROSTENEDIONE âž” ESTRONE (in females) |
Gonadotropins (E.g. FSH, LH, hCG); Age; Obesity; Insulin; Alcohol. |
PROLACTIN Smoking; Anti-mullerian hormone Certain Drugs Finasteride; PROGESTERONE Nettle root Flavonoids |
In females, FSH increases aromatase activity, enhancing this conversion; |
|
Aromatase enzyme converts androgens to estrogens
Androgens ➔ Estrogens
aromatase enzyme
Aromatase is responsible for the production of 18-carbon estrogens from 19-carbon androgen steroids:TESTOSTERONE and ANDROSTENEDIONE - the gene CYP19 encodes the aromatase enzyme (a member of the Cytochrome P450 enzyme superfamily).
ANDROSTENEDIONE ➔ ESTRONE (in women)
(In the female, FSH increases aromatase activity, enhancing this conversion)
TESTOSTERONE ➔ ESTRADIOL
Aromatase production
Different body tissues produceestrogen via aromatase response to different activating promoters. Tissue-specific regulation of CYP19 (aromatase gene) expression is achieved through the use of distinct promoters controlled by hormones and other factors, including:
Aromatase Gene (CYP19) Expression Regulators |
||
|
Location |
Promoter |
Promoter regulated by: |
|
Ovaries |
Cyclic AMP via the proximal promoter II |
FSH |
|
Placenta |
distal promoter I.1 |
Retinoids |
|
Adipose tissue, skin fibroblasts, bone |
distal promoter I.4 |
Glucocorticoids and class 1 cytokines E.g. tumor-derived PGE2 is the major factor stimulating local aromatase expression in the breast fat of cancer patients. |
Aromatase can be found in several tissues
Aromatase ACTIVITY is inhibited by (examples):
Aromatase ACTIVITY is ▲Enhanced by:
Aromatase ACTIVITY is ▼Reduced by:
Aromatase conversion pathway directly affected by:
5α-Reductase converts:
TESTOSTERONE➔ DIHYDROTESTOSTERONE (DHT) (normally in males)
Mainly in peripheral tissue, but also in testes; DHT is significantly more potent than TESTOSTERONE, and thought to be involved in prostate enlargement, prostate cancer and PCOS.
There are two 5AR forms (isoenzymes)
5AR Inhibited by:
At the inner membrane, a series of enzymatic reactions occurs, Enzyme P450SCC converts:
Cholesterol ➔ PREGNENOLONE (in mitochondria)
Production / Activity of P450SCC regulated by:
P450SCC inhibitors include:
3ß-HSD converts:
PREGNENOLONE ➔ PROGESTERONE
DHEA ➔ ANDROSTENEDIONE;
3ß-HSD Production/Activity stimulated by:
3ß-HSD production / activity suppressed by:
3β-HSD pathway by:
17ß-HSD converts:
ANDROSTENEDIONE <=> TESTOSTERONE
ESTRONE (E1) <=> ESTRADIOL (E2)
ESTRADIOL (E2) synthesis occurs principally through oxidation of ESTRONE (E1) - and is a reversible reaction;
The ESTRADIOL (E2) / ESTRONE (E1) ratio before menopause is > 1 - after menopause ESTRONE 1 is the predominant estrogen.
Both ESTRADIOL (E2) and ESTRONE (E1) can be metabolized to the biologically weaker ESTRIOL (E3), and to a number of other metabolites - via A-ring (Anti-carcinogenic) metabolic pathways, E.g, 2-HYDROXYESTRONE and its methylated form 2-METHOXYESTRONE or D-ring (potentially carcinogenic) metabolism E.g, 16α- HYDROXYESTRONE.
Tissue enzymes (E.g sulfatases and 17ß-HSDs) originating in bowel bacterial flora and the intestinal mucosa, activate strogens locally to ESTRADIOL (E2) and ESTRONE (E1). Stanczyk F. Estrogens used for replacement therapy in postmenopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2001;15(suppl 4):17-25.
17ß-HSD pathway directly affected by: