"Everyone should know that most cancer research is largely a fraud and that the major cancer research organizations are derelict in their duties to the people who support them."
- Linus Pauling Ph.D. (Two-time Nobel Prize winner)
"What mechanisms may be putting a cell's aerobic ATP energy production "out of order"?
"What is damaging / mutating DNA to cause altered genetic expression, that allows cancer to proliferate?"
Genes produce enzymes, which control all cell life functions
We are led to believe that carcinogens and mutagens or lifestyle and hereditary factors "predispose" us to genetic defects that cause cancer. The theory is that cancer starts when a defective oncogene (controller gene combined with the loss of a suppressor gene mysteriously results in unrestrained growth. However, genes are stable molecules that account for the stability of life, so how can we have a raging cancer epidemic, with over 6 million new cases per year? There are far too many cancer observations that cannot be answered by the genetic defect theory, including cancer growth itself:
Genes do not control growth any more than a steering wheel controls an automobile.
The steering wheel does not power the automobile, and genes do not cause cells to divide and multiply. Genes control the direction of growth and maintain the continuity of life. Biology texts state that genes have only two functions:
No genes control other genes and none control rate of growth. Genes are composed of DNA. They are combinations of 2 functionally equal nitrogenous base pairs called AT and CG, and there are only 64 possible combinations (codons), known as "The Genetic Code". All gene bases are functionally equal, producing the 20 well-known amino acids used to make protein or to stop and start protein synthesis . No known human genetic defects contribute directly to unrestrained or rapid growth.
| The Genetic Code 101 |
|---|
|
The genetic code is the universal "dictionary" by which genetic information is used to make PROTEINS --- the functional machinery of living organisms. It is a function that determines how a set of nucleotides on messenger RNA (mRNA, a type of RNA, the instructions conveyed from DNA for making proteins) will be turned into a set of amino acids. Nucleotides (in a specific and controlled order) are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Each nucleotide has 3 parts: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. When DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA, the sequence of bases remains exactly the same, except that each thymine (T) is replaced by uracil (U). The nitrogenous base. One of adenine (A), guanine(G), cytosine(C), thymine(T), and uracil (U). A, C and G are found in both RNA and DNA, T is only in DNA and U takes the place of Thymine in RNA. In DNA, the nitrogenous bases form one of two functionally equal base pairs - either AT or CG. Diagram shows all 64 codons in mRNA 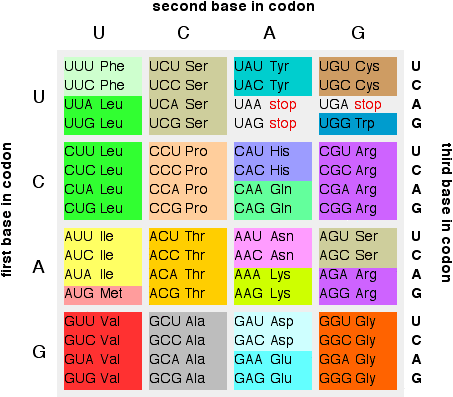
The "words" (codons, nucleotide triplets) of the genetic message are three nucleotides long SInce RNA and DNA each have only 4 bases and a "word" (codon) is 3 nucleotides long, the "dictionary" has only 64 permutations (i.e. 43) possible "words", with U of mRNA codons substituting for T in DNA, when making amino acids according to mRNA instructions. Proteins 61 of these 64 "words" (codons, nucleotide triplets of nitrogenous bases) are utilized by messenger RNA (mRNA, directs protein synthesis) to code for the 20 amino acids, which are then selectively strung together in the cytoplasm (attached on ribosomes) to make different proteins (called polypeptides). Except for methionine (ATG) and tryptophan (TGG), the other 18 amino acids have more than one codon (from 2 to 6) - and the code is therefore called degenerate. Some example amino acids are glycine (GGT), serine (TCT), and valine (GCT). e.g. the polypeptide glycine-serine-valine will read GGT-TCT-GCT. 3 "words" (codons) are used to indicate where a polypeptide stops: TAA, TAG and TGA. The polypeptide "START" is indicated by ATG (the identical codon as methionone). |