Breast Cancer
What are the causes / risk factors of breast cancer?
What measures can I take to prevent breast cancer?
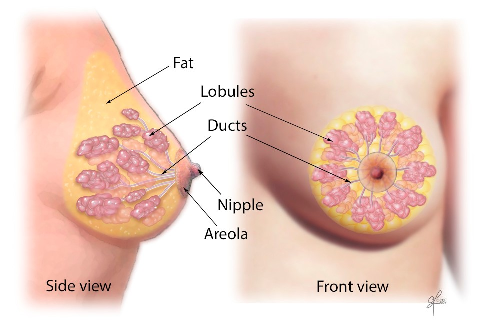
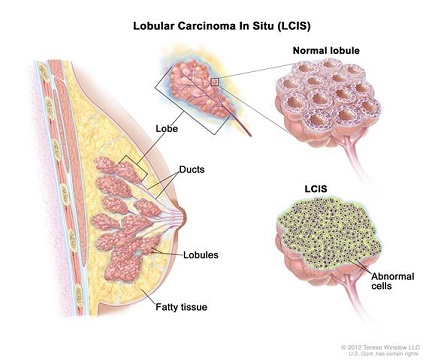
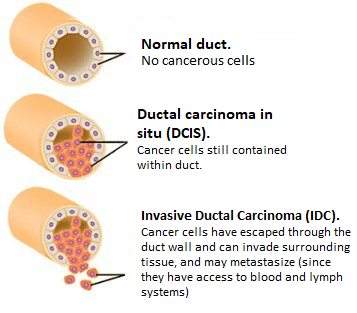
Less common, types of breast cancer include: Medullary, Mucinous, Tubular, Metaplastic, Papillary breast cancer, Inflammatory breast cancer (a faster-growing type, ~1 - 5% of all breast cancers), Paget 's disease (cancer begins in the nipple ducts).
Breast tumour cells can metastasize (i.e. spread) to the axillary lymph nodes and to other organs, most often the bones, brain, liver and lungs. Breast cancer cells can break away from the primary tumor and enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system, where blood or lymph fluids can transport the cells around the body. The cells can then settle and form new tumors in places far from the original tumor. Commonly, doctors diagnose metastatic breast cancer after previously received treatment for an earlier stage (non-metastatic) breast cancer. When invasive surgery cuts into breast tissue to remove a tumor, there is an obvious risk that cancer cells will enter the bloodstream and metastasize.
A 2018 Finnish / Swedish study examining the routes of metastases in breast cancer (by studying cancer cell DNA) found that metastases do NOT spread from axillary lymph nodes. ". . . metastases in the axillary lymph nodes do not seem to spread further to other organs, so even if these metastases can show how aggressive the cancer is, it is not they that cause the spread," says Johan Hartman, Associate Professor at Karolinska Institutet's Department of Oncology-Pathology, one of the researchers who led the study. The study also found that in certain cases an early explosion of cancer cells from the breast tumour simultaneously gives rise to metastases in several different organs. The researchers also showed that different regions of the breast tumours caused metastases in specific organs in the body. Ullah et al, 2018
On a positive note: 80% of identified breast lumps are NON-cancerous.
Globally. Breast cancer is the secondmost common cancer killer of women - only lung cancer is more deadly. Worldwide, in 2022, 2.3 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer, which caused 670,000 deaths. Countries with a high development index (hdi) have up to twice as many breast cancer diagnoses (1 in 12 in their lifetime, and 1 in 71 die of breast cancer) compared to women in a low HDI country (1 in 27 diagnosed, and up to 1 in 48 women die). WHO
In the U.S.
Research at the American Institute of Cancer Research estimated that about 40% of U.S. all cancer cases and about half of the cancer deaths could be prevented by making better lifestyle choices. Modifiable risk factors include cigarette smoking (leading contributor to cancer deaths 32.2% in men, 24.4% in women), body weight, infection, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, diet, stress and uv radiation. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States, 2019, published 2024 in American Cancer Society journal
Paleoanthropological research shows that cancer was virtually nonexistent in humans before poor diet and pollution appeared. Cancer: an old disease, a new disease or something in between?
Iron and aluminum toxicity in breast cancer
Genes do not have the last word. Breast cancer risk increases <10% with a family history of the disease. Mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are said to increase breast cancer risk substantially, however, it is the expression of your genes that dictates the risk, and not simply their existence. Gene expression can be controlled (by whether they are turned on or not) via lifestyle and dietary choices.
| Relative Risk | Factors |
|---|---|
| > 4.0 | Female Age > 65 - although risk increases across all ages until
80; Inherited mutations for breast cancer (BRCA-1 or BRCA-2) 2 or more; 1st-degree relatives diagnosed with BC at an early age; Personal history of BC; High breast tissue density Biopsy confirmed atypical hyperplasia |
| 2.1 - 4.0 | One 1st-degree relative with BC; High dose radiation to chest; High bone density (post-menopausal) |
|
1.1 - 2.0 Factors affecting circulating hormones |
Age >30 years at 1st full-term pregnancy; Menarche before age 12 years; Menopause > 55 years; No full-term pregnancies; Never breast-fed a child; Recent oral contraceptive use; Recent and long-term use of hormone replacement therapy; Postmenopausal obesity |
|
1.1 - 2.0
Other Factors |
Personal history of endometrium, ovary or colon cancer; Alcohol consumption* Tall height; High socio-economic status; Jewish heritage |
* More than 2 alcoholic drinks/day. According to data published in the British Journal of Cancer in 2002, 4% of all breast cancers (~44,000 cases a year) in the United Kingdom are due to alcohol consumption. Could this be due to magnesium depletion in the body consequential to drinking alcohol? See: Magnesium against Cancer
Tumors and calcifications show up white, as does dense breast tissue.
Dense breasts have relatively high amounts of glandular and connective tissue compared to fatty tissue. The diagram below shows increasing levels of glandular / connective tissue density, which can only be seen on mammograms and can not be felt via physical examination. Breasts are classified as dense if they fall into the (C) and (D) classifications:
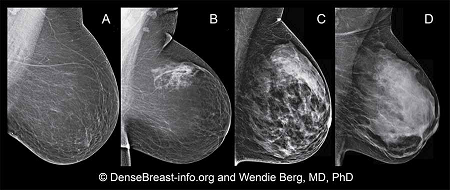
Although often inherited, other factors can influence breast density. Including increasing age, having children and using the estrogen-lowering drug Tamoxifen. Breast tissue density is also associated with having a low body mass and using postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
Having dense breast tissue does not increase death rate from breast cancer. Although having high breast tissue increases risk for breast cancer, research shows that a woman with dense breast tissue is no more likely to die from breast cancer than a woman with fatty breast tissue.
Double blind, placebo controlled, randomized study used transdermal progesterone and estradiol on 40 premenopausal women undergoing breast surgery for the removal of a lump. The study examined results of two breast biopsies, one at the beginning of the study and another 13 days later. Estrogen and the progesterone did not show up in the serum, but showed up in the breast tissue at over 100% increased levels above placebo. Chang et al, 1995
Results of breast tissue cell proliferation from biopsies after 13 days transdermal progesterone or estradiol administration:
| Method of Measuring Cell Proliferation ▼ | Placebo | Progesterone | Estradiol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitosis per 1000 Cells | 0.51 | 0.17 | 0.83 |
| PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) - the most accurate method | 7.8 | 1.9 | 17.4 |
Study concluded that in normal breast tissue:
Based on PCNA numbers (PCNA presence in actively growing and dividing cells serves as a marker for such cells):
progesterone levels naturally decrease with age. In women this decrease occurs about the age of 35 and men about ten years later. progesterone balances estrogen, such that an imbalance of estrogen over progesterone could be responsible for increased cell proliferation in estrogen-sensitive breast cancer.
Supplement with Iodine. Prevents cancer formation and spread, especially reproductive organ cancers;
Excess ironcontributes to oxidant activity. Ferritin, the iron transport protein, tends to increase after menstruation ceases; should not be above 80; donating blood lowers ferritin level;
Iron and Aluminum toxicity in breast cancer
They do not save lives!
Instead, do regular self-examinations of breasts or find a doctor who does thermography- this non-invasive method is based on heat detection, does not compress breast and does not use harmful radiation, which can actually cause breast cancer over time.
Take a daily 20-30 minute brisk walk
There are several tactics you can use to reduce estrogen in the body:
How to reduce body's estrogen levels
For example:
DIM - Estrogen - blocker with anti - cancer benefits
Chang KJ, Lee TTY , Linares-Cruz G, Fournier S, de Lignieres B (1995) Influences of percutaneous administration of estradiol on human breast epithelial cell cycle in vivo. Fertility and Sterility; 63; 7865-7891. Online link
Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Familial breast cancer: collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 52 epidemiological studies including 58,209 women with breast cancer and 101,986 women without the disease. Lancet. 2001;358(9291):1389–1399. PubMed
Ikram Ullah, Govindasamy-Muralidharan Karthik, Amjad Alkodsi, Una Kjällquist, Gustav Stålhammar, John Lövrot, Nelson-Fuentes Martinez, Jens Lagergren, Sampsa Hautaniemi, Johan Hartman, Jonas Bergh (2018) Evolutionary history of metastatic breast cancer reveals minimal seeding from axillary lymph nodes. Journal of Clinical Investigation; DOI: 10.1172/JCI96149
Ullah I, Karthik GM, Alkodsi A, Kjällquist U, Stålhammar G, Lövrot J, Martinez NF, Lagergren J, Hautaniemi S, Hartman J, Bergh J. Evolutionary history of metastatic breast cancer reveals minimal seeding from axillary lymph nodes. J Clin Invest. 2018 Apr 2;128(4):1355-1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI96149. Epub 2018 Feb 26. PMID: 29480816; PMCID: PMC5873882. PubMed