Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the U.S. and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occurs in skin often exposed to sunlight. E.g. the face, neck, and hands. It especially occurs in fair-skinned and fair-haired people, those who had freckles as a child and those who have blue eyes.
Has several functions:
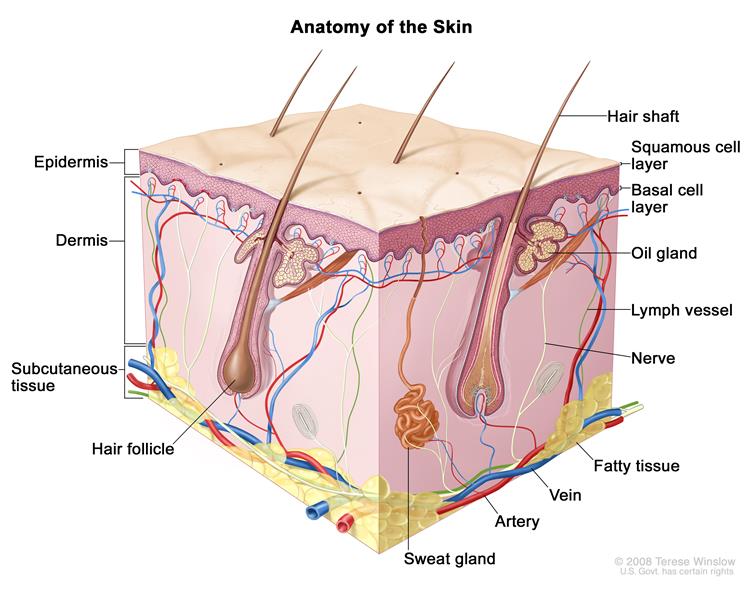
The thickness of a sheet of paper, varies somewhat according to site, the epidermis is the topmost layer of our skin, and the first line of defense against the air and UV light, constantly subjected to damage from oxidative stress.
Its main cell types are:
The dermis is less dense than the epidermis. It contains connective tissue, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands. nerves, hair follicles, and other structures.
Its main cell types are:
This layer hosts fat, connective tissues, large blood vessels and various nerves. Its primary function is to insulate the body to regulate body temperature
Classified as UV-A , UV-B or UV-C (<280 nm) according to its wavelength. Lower wavelength UV-B and UV-C are absorbed by the ozone layer. Only higher wavelength UV-B and UV-A reach us at ground level:
Accounts for 95% of sun's UV rays but although UV-A has less energy than UV-B, (1) its longer wavelength allows it to travel deeper into the skin through the epidermis and into the dermis (2 it is less absorbed by skin components and (3) its lower energy limits its DIRECT damaging effect on them. UV-A penetrates the ozone layer, clouds and 70-90% can pass through glass.
Prolonged UV-A exposure from sunlight (or tanning beds) is now known to cause INDIRECT, oxidative damage to proteins, lipids and DNA in both the epidermal and dermal cells leading to DNA mutations / skin cancer (Including malignant melanoma) and prematurely aging skin. Link. UV-A radiation disturbs the redox (oxidant / antioxidant) balance in skin cells, causing oxidative damage by creating reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen, which impair the body's inherent antioxidant systems, e.g. glutathione-glutathione peroxidase and thioredoxin.
Tanning / damaging effect of UV-A is immediate and the body does not alert us to what is happening with pain. UV-A damage to the dermis can cause second-degree sunburn, where blisters develop on sunburned skin and may take weeks to heal.
Only 5% of the UV radiation reaching us from the sun, but UV-B has higher energy levels than UV-A and although 99.9% is absorbed by melanin in melanocytes (cells in the skin's outer layer - the epidermis) and their DNA, DIRECT damage caused by the other 0.1% can damage DNA and cause first degree sunburn in the epidermis, which usually heals in a few days. An estimated 80% of the serious skin disorders are attributed to prolonged exposure to UV-B.
UV-B stimulates skin cells, called melanocytes, to produce melanin, the pigment in skin that protects against UV-exposure. Tanning is usually delayed. However, prolonged UV-B exposure can cause oxidative damage to cellular DNA in the epidermal cells, which can can lead to skin cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and melanoma
UV-B is mostly blocked by glass
UV-B converts 7-dehydro-Cholesterol (7-DHC) in the lower epidermis and dermis layers of the skin to vitamin D3.

Oxidative damage to proteins with disrupted structures would be targeted for degradation by the cellular proteolytic systems, which in turn may enhance apoptotic events. Costa V., Quintanilha A., Moradas-Ferreira P. Protein oxidation, repair mechanisms and proteolysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. IUBMB Life. 2007;59:293–298. doi: 10.1080/15216540701225958. PubMed
A gene is the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid, an organic chemical) sequence which houses the genetic information to make a protein. To synthesize protein, the cell uses RNA, which shares a similar structure to DNA..
Those who have:
Flat squamous cells form the outermost layer of the epidermis. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a.k.a. "rat-bite" tumor, is diagnosed when these cells become abnormal and grow out of control. SCC sometimes develops from a precancerous skin growth called an actinic keratosis. SCC is usually seen as scaly red patches or open sores, which may crust and bleed. Characteristically it looks elevated with a central hole. Allowed to grow, it can be fatal.
Bowens disease is a form of squamous cell cancer in situ.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer in the U.S. and the most common skin cancer. 90% of the epidermal cells, so named because they are found in its basal layer, below the squamous cells. These round cells are also called keratinocytes. BCC is usually benign i.e. a relatively harmless skin cancer. It typically looks like a red patch, scar, shiny bump, pink growth or an open sore, which can bleed, ooze or crust. Rarely spreads or metastasizes, but should not be ignored since it is more easily treated whilst small.
Melanoma is a skin cancer involving the uncontrolled growth of melanocytes (cells In the lower epidermis of the skin, that produce melanin) - the pigment that gives skin its color, made darker when exposure to the sun triggers melanocytes to make more melanin pigment to absorb UV rays to protect the skin. The difference between melanoma in situ and invasive melanoma is the extent of its growth. Melanocytes are synthesized by melanosomes.
Melanoma begins in the skin's outer layer, called the epidermis, occurring in such as back, neck, arms, legs, scalp, face, soles of feet and palms. Melanoma can also occur in other areas of the body, such as the mucous membranes accounting for 1.4% of melanoma.(incidence rates have been stableover time,non-keratinized and moist, inside mouth, nose, vagina, anus), and eyes (called occular melanoma), and just about anywhere in the body if it becomes invasive.
Melanoma in situ. In initial stage 0 melanoma is in the epidermis (thin top layer) of skin and stays in situ.. 1.4% of melanoma.
Invasive melanoma. Stages 1 - 4 are called invasive melanoma, with each stage going deeper. At stage 3, it has penetrated the basement membrane to enter the lower level of skin, called the dermis. With access to lymph tissue, blood vessels and nerves, the melanoma cells can travel to body organs, such as liver or lungs, distant lymph nodes, and the central nervous system, at which point it is defined as stage 4 / metastatic melanoma. Catching melanoma in its early stages is crucial, since the 5 year survival rates are around 99% for stages 0,1, and 2 but drop dramatically to ~75% for stage 3 and ~35% for stage 4

DNA in melanin-producing cells becomes damaged, which if not repaired by the immune system, causes cells to multiply out of control forming malignant tumors. Study in 2020 reported >90% of melanoma cases in the United States are attributable to UV radiation, affected by UV index and geographical location.
The sun can damage DNA in skin cells, which if not repaired by the immune system, can cause skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. Curable if detected early, but each year in the U.S. ~8,000 people die of this type of cancer (2023), the most fatal of cutaneous cancers. Here's the interesting fact though - a significant percentage of melanoma, sometimes aggressive, is not related to UV radiation, and can even occur in places where the sun doesn't shine.
Melanomas are not always dark colored. Rarely, they can be pink or skin-colored. Watch out for a spot on the skin that looks different to other spots - the "ABCDE" signs, which may indicate melanoma, but not all have to be present:
In uveal melanoma - the role of ultraviolet (UV) light is more controversial, but likely contributes to at least a subset of cases
Cause of DNA damage is not usually UV light. What is causing the damage is still under investigation - could be related to trauma.
Mucosal melanomas. Occur on mucus membranes on cavities exposed to the outside of the body, inside the nose, mouth, rectum, eyelids, and vagina. These melanomas are not caused by direct UV exposure.
Acral (means extremity) lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is a subtype of cutaneous melanoma (lentiginous means the melanoma spot is darker than the skin surrounding it and has a sharp border presenting a stark contrast to the lighter skin around it). ALM most commonly occurs on palms or soles of feet, and can also occur under the finger or toenails (called subungual AM), in which discoloration (general, spots or lines) extends to the cuticle and can cause the nail to crack or break in its advanced stage. ALM may stem from physical stress / injury, suggested by its propensity for the bottom of the feet, which undergo pressure from weight or tight shoes or wearing high heels. PubMed Subungual hematomas are when an injury causes blood to be trapped under the nail and looks different to subungual melatoma in that it looks more like a dark smudge or bruise under the nail. ALM represents only 2-3% of melanomas in Western populations, but is the most common type of melanoma in non-Caucasians with darker skin (namely those of Hispanic, African, or Asian heritage). In Asian countries such as Taiwan, China, Japan, Korea, Hong Kong, and Singapore, AM has been reported to account for up to 58% of all melanomas. PubMed

Melanoma under the nail. Watch for a dark band > 3mm in width or a spot that looks fuzzy around the edges.
Omega-3 has an important role in restoring skin damage caused by UV-B. A study exposing mice to UV-B found that Omega-3 in their diet reduced epidermal damage caused by UV-B and suppresses excessive epidermal water loss (UV-B typically disrupts the stratum corneum's ability to retain water - whose moisture is an anti-inflammatory protection against environmental stress). The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis.
Being written