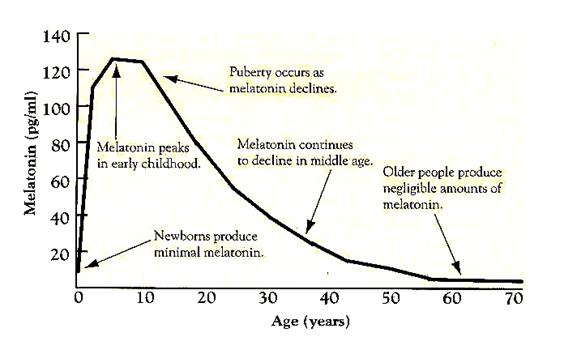
Young child. Nighttime levels reach a peak in children between on average 3 to 5 (another source says 1-3) years of age (may explain their tendency to sleep longer than adults) and decrease steadily throughout puberty. The abundant MELATONIN levels in children are believed to inhibit sexual development.
Puberty. By the end of puberty, peak MELATONIN levels have decreased significantly.
Adult. Levels continue to fall steadily throughout adult life.
Old age. Lower levels are seen in old age.
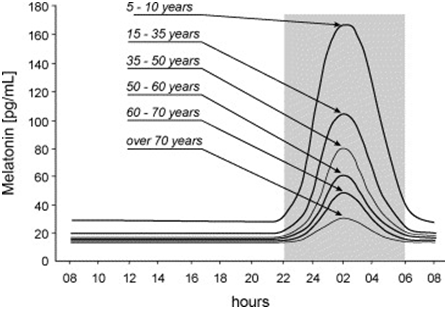
Circadian profiles of serum MELATONIN concentrations at various ages
Gray area=Darkness.
Dr. George Brainard experimented on 600 healthy volunteers
- Blue light significantly lowered MELATONIN production. Studies at 2:00 am (when MELATONIN levels at peak) exposed dilated pupils to different wavelengths of monochromatic light (only one color) over 90 minutes, found that the short wavelength in the blue portion of the visible spectrum was most potent at lowering MELATONIN production.
- Special retinal photoreceptor regulates MELATONIN production. It was revealed that it is not the visual rod and cone photoreceptor mechanism of the eye that is regulating pineal MELATONIN production, but that a novel photoreceptor in the retina was responsible. Only 0.5-1.7 foot-candles of blue-green light (509nm) and 10 foot-candles of broad-band white light can lower MELATONIN production under tightly controlled exposure conditions.
The pineal gland calcifies over time as a consequence of incorporating fluoride. During the late 1990's, scientist Jennifer Luke of the University of Surrey, England, was the first to study of the effects of sodium fluoride on the pineal gland. She determined that the pineal gland was a target for fluoride, absorbing more fluoride than any other physical matter in the body, even bones. The pineal gland is unique in that it can be classified as a soft or as a mineralizing tissue.
The result of 50 years of prophylactic fluorides in dentistry is that the aged pineal contains more fluoride than any other normal soft tissue. Significantly higher than in muscle. In terms of mineralized tissue, the mean fluoride concentration in the pineal calcification was equivalent to that in severely fluorosed bone and more than 4x higher than in corresponding bone ash,

Given the pineal gland's importance to the endocrine system, its calcification would block endocrine activity. Providing an explanation of the physiological damage caused by sodium fluoride. Fortunately, a fluoride calcified pineal gland can be stimulated by frequent exposure to outdoor sunshine, 20 minutes or so at a time.
Nine Life Choices for Vibrant Health
Attend to Diet, Lifestyle & Emotional State
Present in most health problems


"The medical kit of the future"